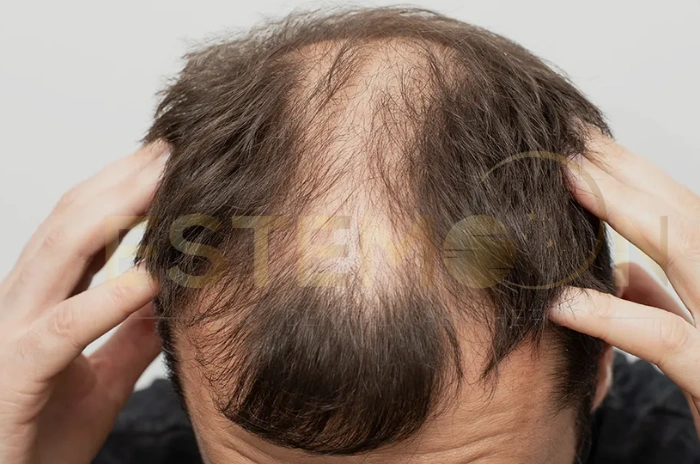
Vellus hair, commonly known as “peach fuzz,” is a natural component of human hair growth that often raises questions about its purpose and whether it should be removed. This fine, light-colored hair appears across most of the human body and serves important biological functions that many people don’t fully understand.
At Estemoon, we recognize that decisions about vellus hair removal should be based on accurate information about its biological role, removal methods, and potential consequences. Many individuals seek treatment without understanding the difference between vellus and terminal hair, or the implications of various removal techniques on skin health and hair regrowth patterns.

What Vellus Hair Is and What Peach Fuzz Means
Vellus hair represents a specific type of human hair characterized by its fine texture, light pigmentation, and short length. This hair type differs significantly from terminal hair in both structure and function, serving unique biological purposes across the human body.
Structural Characteristics: Vellus hairs are typically less than 2 centimeters in length and lack the medulla (central core) found in terminal hairs. The hair shaft diameter measures approximately 30 micrometers or less, making these hairs nearly transparent and barely visible to the naked eye under normal lighting conditions.
Pigmentation Properties: Most vellus hairs contain minimal melanin pigment, giving them a colorless or very light appearance. This lack of pigmentation contributes to the “peach fuzz” appearance, particularly on facial areas where the hair is most noticeable against skin contrast.
Understanding Vellus Hair and Its Purpose on Your Body
Vellus hair serves multiple important biological functions that contribute to overall skin health and body temperature regulation, despite its seemingly insignificant appearance.
Thermoregulation Functions: Vellus hairs play a crucial role in maintaining body temperature through several mechanisms. They trap a thin layer of air close to the skin surface, providing insulation that helps retain body heat in cool conditions while allowing heat dissipation when temperatures rise.
Sensory Enhancement: The fine structure of vellus hairs makes them highly sensitive to air currents and light touch, functioning as early warning systems for the nervous system. This sensory capability helps detect environmental changes, potential threats, or gentle contact that might otherwise go unnoticed.
Skin Protection: Although individually fragile, vellus hairs collectively provide a protective barrier against environmental irritants, UV radiation, and minor physical trauma. This protection is particularly important on exposed skin areas like the face and arms.
Where Vellus Hair Grows on the Body
Vellus hair distribution follows specific patterns across the human body, with variations based on age, gender, hormonal status, and individual genetic factors.
Universal Distribution Areas:
- Facial regions: Cheeks, forehead, and areas not covered by terminal hair growth
- Upper body: Shoulders, upper arms, and chest (areas without terminal hair)
- Lower extremities: Legs and feet, particularly in women and children
- Trunk areas: Back, abdomen, and sides where terminal hair is absent
Gender-Specific Patterns: Women typically retain more extensive vellus hair coverage throughout adulthood, particularly on facial areas, arms, and legs. Men often experience vellus-to-terminal hair conversion in response to androgenic hormone activity, reducing vellus hair coverage in certain body regions.
| Body Region | Typical Coverage | Hormonal Sensitivity | Gender Differences |
|---|---|---|---|
| Face | Moderate to high | Very high | More prominent in women |
| Arms | High | Moderate | Similar distribution |
| Legs | High | Moderate | More retained in women |
| Torso | Variable | High | Significant male conversion |
Vellus vs Terminal Hair: Key Differences
Understanding the distinctions between vellus and terminal hair is essential for making informed decisions about hair removal treatments and setting realistic expectations for outcomes.
Structural Differences: Terminal hairs contain three distinct layers: the cuticle (outer protective layer), cortex (main structural component), and medulla (central core). Vellus hairs lack the medulla and have a much thinner cortex, making them structurally weaker and less pigmented.
Growth Characteristics:
- Terminal hair: Long growth phase (2-7 years), can grow several inches or more
- Vellus hair: Short growth phase (weeks to months), maximum length under 2 cm
- Diameter: Terminal hairs measure 60-100 micrometers; vellus hairs under 30 micrometers
Pigmentation Levels: Terminal hairs contain substantial melanin deposits that create visible coloration ranging from blonde to black. Vellus hairs contain minimal pigment, appearing nearly transparent or very light regardless of the person’s natural hair color.
Follicle Structure: Terminal hair follicles extend deep into the dermis and hypodermis, with large, active sebaceous glands. Vellus hair follicles remain superficial with smaller, less active sebaceous glands that produce minimal sebum.
Response to Treatments: Terminal hairs respond well to laser hair removal due to their high melanin content, while vellus hairs often show poor response to light-based treatments. This difference significantly impacts treatment planning and outcome expectations when working with intermediary organizations.

What Causes the Growth of Fine Vellus Hair
Several factors influence vellus hair growth patterns, density, and characteristics, ranging from genetic predisposition to hormonal fluctuations and environmental influences.
Genetic Determinants: Individual genetic makeup largely determines baseline vellus hair distribution, density, and growth patterns. Some people naturally have more prominent vellus hair due to inherited traits that affect follicle sensitivity and hair production capacity.
Hormonal Influences:
- Androgens: Can convert vellus follicles to terminal hair production
- Estrogens: Help maintain vellus hair characteristics
- Thyroid hormones: Affect overall hair growth rates and quality
- Growth hormone: Influences follicle development and hair production
Age-Related Factors: Vellus hair patterns change significantly throughout life stages. Newborns have extensive vellus coverage that gradually changes during childhood, undergoes major modifications during puberty, and may alter again during aging processes.
Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions can affect vellus hair growth, including hormonal disorders, autoimmune conditions, nutritional deficiencies, and metabolic diseases. These conditions may increase or decrease vellus hair production depending on their specific effects on follicle function.
Medication Effects: Some medications can influence vellus hair growth by altering hormone levels, affecting blood circulation, or directly impacting follicle activity. Hormonal treatments, chemotherapy drugs, and certain cardiovascular medications may cause changes in hair growth patterns.
Environmental Factors: Sun exposure, climate conditions, and skincare routines can influence vellus hair appearance and growth. UV radiation may affect hair pigmentation and structure, while certain topical treatments can alter follicle activity.
Is Laser Hair Removal an Effective Treatment for Peach Fuzz
Laser hair removal shows limited effectiveness for vellus hair removal due to the fundamental differences between vellus and terminal hair characteristics, particularly regarding pigmentation and follicle structure.
Technical Limitations: Laser hair removal relies on melanin absorption to generate heat that damages hair follicles. Since vellus hairs contain minimal melanin, they absorb insufficient laser energy to achieve effective follicle destruction. This technical limitation makes laser treatment poorly suited for vellus hair removal.
Treatment Outcomes:
- Limited effectiveness: Most vellus hairs show minimal response to laser treatment
- Inconsistent results: Some fine hairs may be reduced while others remain unchanged
- Temporary effects: Any reduction achieved is often temporary rather than permanent
- Risk of paradoxical growth: Some individuals experience increased hair growth following laser treatment
Alternative Approaches: More effective methods for vellus hair removal include:
- Dermaplaning: Professional blade removal that also exfoliates dead skin
- Threading: Precise hair removal technique suitable for facial areas
- Waxing: Can remove fine hairs but may cause irritation
- Chemical depilatories: Dissolve hair shafts but don’t affect follicles
Professional Consultation Importance: Working with qualified intermediary organizations helps determine the most appropriate treatment approach based on individual hair characteristics, skin sensitivity, and desired outcomes. Professional assessment can prevent ineffective treatments and potential complications.
Should You Remove Peach Fuzz
The decision to remove vellus hair involves weighing cosmetic preferences against potential benefits and risks, considering individual circumstances and long-term implications.
Potential Benefits of Removal:
- Smoother makeup application: Removing vellus hair can create a smoother surface for cosmetic application
- Enhanced skin appearance: Some individuals prefer the look of hair-free skin
- Improved skincare absorption: Removal may enhance topical product penetration
- Personal confidence: Meeting individual aesthetic preferences
Possible Drawbacks:
- Loss of natural functions: Elimination of thermoregulation and sensory benefits
- Increased sensitivity: Removal may increase skin sensitivity to environmental factors
- Potential irritation: Removal methods can cause temporary or chronic skin irritation
- Regrowth maintenance: Most methods require regular repetition
Individual Considerations:
- Skin sensitivity: Those with sensitive skin may experience adverse reactions
- Hair density: Individuals with minimal vellus hair may see little benefit from removal
- Lifestyle factors: Active individuals may benefit more from vellus hair’s protective functions
- Medical conditions: Certain skin conditions may be worsened by hair removal
Method Selection Factors:
| Method | Effectiveness | Duration | Skin Impact | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dermaplaning | High | 3-4 weeks | Minimal | Moderate |
| Threading | High | 2-3 weeks | Minimal | Low |
| Laser | Low | Variable | Minimal | High |
| Shaving | Moderate | 1-2 weeks | Potential irritation | Very low |
Professional Guidance: Consultation with intermediary organizations provides personalized assessment of removal options, skin suitability, and expected outcomes. Professional guidance helps avoid inappropriate treatments and ensures safe, effective approaches tailored to individual needs.
FAQ
What is the purpose of vellus hair?
Vellus hair serves multiple important biological functions including temperature regulation by trapping air for insulation, enhancing sensory perception of light touch and air currents, providing protection against UV radiation and environmental irritants, and helping distribute natural skin oils (sebum) across the skin surface for moisture and barrier function.
Is it safe to remove vellus hair?
Removing vellus hair is generally safe when done properly, but it eliminates the natural protective and regulatory functions these hairs provide. Removal methods can cause temporary irritation, and individuals lose the benefits of temperature regulation and enhanced sensory perception. People with sensitive skin should exercise particular caution and consider professional consultation.
Does laser hair removal work on vellus?
Laser hair removal is largely ineffective on vellus hair because these fine hairs contain insufficient melanin pigment to absorb the laser energy needed for follicle destruction. Most vellus hairs show minimal response to laser treatment, and results are typically temporary when any reduction occurs. Alternative methods like dermaplaning or threading are more effective for vellus hair removal.
Does shaving peach fuzz make it thicker?
Shaving does not make vellus hair grow back thicker or darker. This is a common misconception based on the blunt tip created by cutting, which may feel coarser initially. The hair follicle structure and genetic programming remain unchanged by shaving, so regrown vellus hair maintains its original fine, light characteristics. However, shaving may cause temporary skin irritation in some individuals.
Follow us on social media for updates, tips, and patient success stories: