Male hair loss affects millions of men worldwide, causing significant psychological distress and impacting self-confidence. Treating baldness in men has evolved dramatically over the past decades, with scientifically proven treatments now available to combat this common condition.
This comprehensive guide explores evidence-based solutions for male pattern baldness, examining the most effective medications, treatment protocols, and what men can realistically expect from modern hair loss interventions. Understanding these options empowers men to make informed decisions about their hair restoration journey.
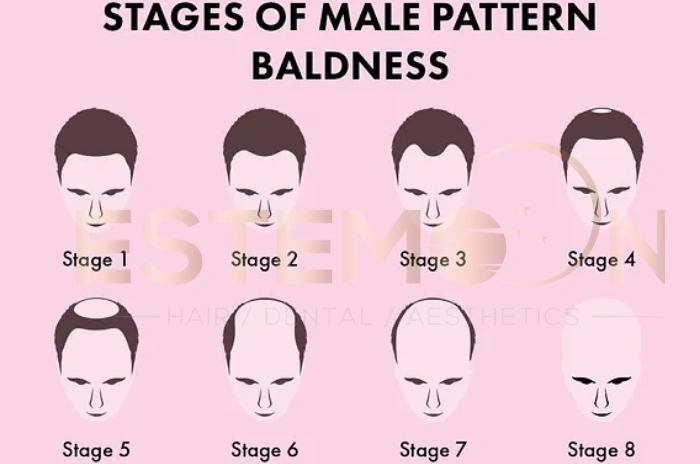
Understanding Male Pattern Baldness and Its Causes
Male pattern baldness, medically known as androgenetic alopecia, represents the most common form of hair loss in men, affecting up to 95% of men experiencing hair thinning. This hereditary condition typically begins with a receding hairline and crown hair loss, progressing in predictable patterns over time.
The primary culprit behind this condition is dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone derived from testosterone. DHT binds to hair follicles, particularly those on the scalp’s crown and temples, causing them to shrink progressively. This miniaturization process shortens the hair growth cycle, producing increasingly thin and weak strands until follicles eventually stop producing hair altogether.
Genetics play a crucial role in determining susceptibility to male pattern baldness. Men with family histories of baldness on either maternal or paternal sides face higher risks of developing this condition. Age also significantly impacts hair loss progression, with most men experiencing some degree of thinning by their 50s.
Key Risk Factors for Male Pattern Baldness
| Risk Factor | Impact Level | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Genetics | High | Family history on both sides increases risk |
| Age | High | Progressive worsening with advancing age |
| DHT Sensitivity | High | Individual follicle sensitivity varies |
| Hormonal Changes | Medium | Testosterone fluctuations affect progression |
| Stress | Low-Medium | Chronic stress may accelerate hair loss |
Environmental factors and lifestyle choices can influence the severity and progression rate of hair loss. Chronic stress, poor nutrition, smoking, and certain medications may exacerbate thinning hair conditions, though they rarely cause male pattern baldness independently.
Effective Hair Loss Treatments Finasteride and Minoxidil
Modern medicine offers two FDA-approved medications specifically designed for treating baldness in men: finasteride and minoxidil. These treatments represent the gold standard in hair loss treatment, with extensive clinical research supporting their efficacy and safety profiles.
How Finasteride Works
Finasteride operates as a DHT blocker, specifically inhibiting the enzyme 5-alpha reductase that converts testosterone to DHT. By reducing DHT levels in the scalp by up to 70%, finasteride effectively slows hair loss progression and can promote regrow hair in many patients.
Clinical studies demonstrate that finasteride prevents further hair loss in 90% of men and promotes hair regrowth in approximately 65% of users. The medication works best for crown thinning and early-stage receding hairline patterns, showing less effectiveness in completely bald areas.
The standard dosage is 1mg daily, taken orally regardless of meals. Results typically become noticeable after 3-6 months of consistent use, with maximum benefits appearing after 12-24 months of treatment.
How Minoxidil Works
Minoxidil functions as a vasodilator, improving blood circulation to hair follicles and extending the growth phase of the hair cycle. This topical treatment stimulates dormant follicles and increases hair shaft diameter, creating the appearance of thicker, fuller hair.
Available in 2% and 5% concentrations, minoxidil suits various hair loss severities. The 5% solution shows superior results for most men, though some may prefer the 2% formulation to minimize potential side effects like scalp irritation.
Application involves spreading the solution directly onto the scalp twice daily, focusing on thinning areas. Like finasteride, minoxidil requires 3-6 months for visible results, with continued use necessary to maintain benefits.
Combination Therapy Benefits
Many practitioners recommend combining finasteride and minoxidil for hair loss treatment, as these medications work through different mechanisms. This dual approach often produces superior results compared to monotherapy, addressing both the hormonal causes and circulatory aspects of hair loss.
Research indicates that combination therapy can increase treatment success rates by 15-20% compared to using either medication alone. This synergistic effect makes the combination approach particularly valuable for men with moderate to severe male pattern baldness.
Who is a Suitable Candidate for Baldness Treatment
Not every man experiencing hair loss represents an ideal suitable candidate for hair treatment. Several factors determine treatment appropriateness, including age, hair loss pattern, overall health status, and realistic expectations about outcomes.
Ideal Candidates for Treatment
Men aged 18-65 experiencing early to moderate male pattern baldness typically respond best to medical treatments. Those with recent hair loss onset (within 2-5 years) often achieve better results than men with longstanding baldness, as follicles remain more responsive to intervention.
Specific hair loss patterns also influence treatment success. Men with crown thinning and mild receding hairline patterns usually experience better outcomes than those with extensive frontal baldness or completely bald areas where follicles have been dormant for extended periods.
Good overall health status is essential for safe treatment. Men without significant cardiovascular issues, liver problems, or hormone-sensitive conditions generally qualify for both finasteride and minoxidil therapy.
Factors That May Limit Treatment Success
| Limiting Factor | Impact on Treatment | Alternative Options |
|---|---|---|
| Advanced age (>65) | Reduced follicle response | Lower expectations, combination therapy |
| Extensive baldness | Limited regrowth potential | Hair transplant consideration |
| Poor health status | Medication contraindications | Topical treatments only |
| Unrealistic expectations | Treatment disappointment | Counseling, education |
Men with completely bald scalps or those who lost hair more than 10 years ago may see limited regrowth, though treatments can still prevent further progression. Setting realistic expectations is crucial for treatment satisfaction.
Special Considerations
Younger men (18-25) require careful evaluation, as early aggressive treatment may yield excellent long-term results. However, commitment to lifelong treatment and potential side effect concerns must be thoroughly discussed.
Men planning to father children should understand finasteride’s potential impact on male fertility, though current evidence suggests minimal risk. Consultation with healthcare providers helps weigh benefits against potential concerns.
Effective Hair Loss Treatments for Men
Beyond the primary medications, several additional hair loss treatments for men offer promising results either as standalone therapies or adjuncts to traditional treatments. These approaches range from advanced topical formulations to innovative procedural interventions.
Advanced Topical Treatments
Modern formulations combine multiple active ingredients to enhance treatment efficacy. Topical finasteride offers an alternative for men experiencing systemic side effects from oral medication, delivering targeted DHT suppression with minimal systemic absorption.
Compound formulations containing minoxidil, finasteride, and additional ingredients like tretinoin, azelaic acid, or copper peptides may provide enhanced results. These custom preparations require compounding pharmacy preparation but offer personalized treatment approaches.
Hair loss prevention strategies also include specialized shampoos containing ketoconazole, an antifungal agent with anti-DHT properties. While not primary treatments, these products can complement medical therapy and improve scalp health.
Procedural and Device-Based Treatments
Low-level laser therapy (LLLT) devices offer FDA-cleared treatment options for male pattern baldness. These devices use specific light wavelengths to stimulate cellular activity in hair follicles, promoting growth and improving hair density.
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections represent an emerging treatment utilizing concentrated growth factors from the patient’s own blood. While research continues, initial studies suggest PRP may enhance hair growth when combined with traditional medications.
Microneedling procedures create controlled scalp micro-injuries, potentially improving minoxidil absorption and stimulating natural healing responses that promote hair growth. This technique shows particular promise when performed professionally in clinical settings.
Nutritional and Lifestyle Support
Comprehensive hair regrowth for men programs often include nutritional optimization. Key nutrients like biotin, iron, zinc, and vitamin D support healthy hair growth, though deficiencies must be documented before supplementation.
Lifestyle modifications including stress management, adequate sleep, and avoiding harsh hair treatments complement medical therapy. While these factors rarely cause male pattern baldness, they can influence treatment success and overall hair health.
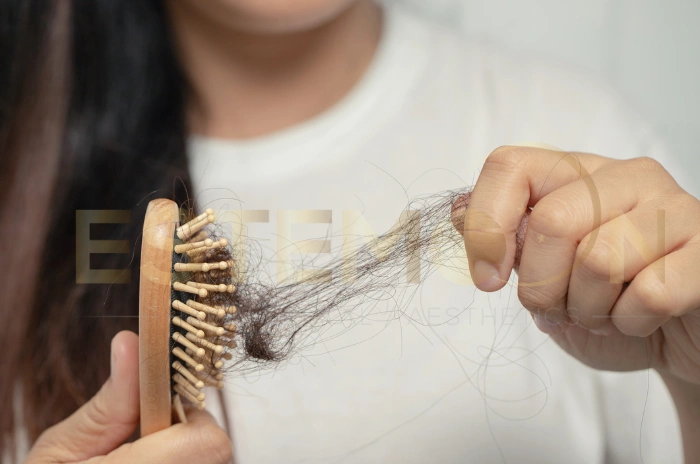

Possible Side Effects of Hair Loss Medications
Understanding the side effects of hair loss drugs enables informed decision-making and appropriate monitoring during treatment. Both finasteride and minoxidil generally demonstrate good safety profiles, though potential adverse effects warrant consideration.
Finasteride Side Effects
Sexual side effects represent the most commonly reported concerns with finasteride use. Clinical trials indicate that 2-4% of men experience decreased libido, erectile dysfunction, or ejaculatory disorders during treatment. These effects typically resolve upon discontinuation and may improve with continued use.
A small percentage of men report persistent sexual side effects after discontinuing finasteride, though the actual incidence and causation remain subjects of ongoing research and debate within the medical community.
Other potential finasteride side effects include breast tenderness, mood changes, and very rarely, allergic reactions. Regular monitoring with healthcare providers helps identify and manage any adverse effects promptly.
Minoxidil Side Effects
Topical minoxidil generally produces fewer systemic side effects than oral medications. The most common adverse effects include scalp irritation, itching, and dryness at application sites. These reactions often improve with continued use or switching to lower concentrations.
Some men experience increased hair shedding during the first 2-4 weeks of minoxidil treatment. This temporary effect, known as “minoxidil shedding,” actually indicates treatment efficacy as weak hairs are replaced by stronger ones.
Rarely, minoxidil may cause unwanted facial hair growth, particularly if solution accidentally contacts facial skin. Careful application and proper hand washing minimize this risk.
Monitoring and Management Strategies
| Side Effect Category | Monitoring Frequency | Management Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Sexual (Finasteride) | Every 3-6 months | Dose adjustment, discontinuation if severe |
| Scalp Irritation (Minoxidil) | Monthly initially | Concentration reduction, moisturizer use |
| Systemic Effects | Annually | Comprehensive health assessment |
Healthcare providers should conduct regular follow-ups during the first year of treatment, with annual monitoring thereafter for stable patients. This approach ensures optimal treatment outcomes while minimizing adverse effects.
How to Get a Prescription for Hair Loss Treatment
Accessing how to get finasteride prescription and other hair loss treatments for men involves several pathways, each with distinct advantages and considerations. Understanding these options helps men choose the most appropriate route for their circumstances.
Traditional Healthcare Routes
Primary care physicians represent the most common starting point for baldness treatment for men. These providers can assess overall health status, review medical history, and determine treatment appropriateness. They can prescribe both finasteride and recommend over-the-counter minoxidil.
Dermatologists offer specialized expertise in hair and scalp conditions, providing comprehensive evaluations and advanced treatment options. Their training includes recognizing various hair loss types and selecting optimal treatment combinations for individual patients.
Endocrinologists may be appropriate for men with suspected hormonal imbalances contributing to hair loss. These specialists can evaluate testosterone levels, thyroid function, and other hormonal factors affecting hair growth.
NHS Hair Loss Treatment Options
The National Health Service provides limited coverage for hair loss treatments, primarily focusing on cases with underlying medical conditions or significant psychological distress. Most cosmetic hair loss treatments require private payment.
NHS providers may prescribe finasteride for men meeting specific criteria, though availability varies by region. Patients should consult their GP to understand local policies and eligibility requirements.
Online and Telemedicine Services
Modern telemedicine platforms offer convenient access to hair loss treatment prescriptions through virtual consultations. These services typically involve completing medical questionnaires and consulting with licensed providers via video or phone.
Reputable online services require comprehensive medical screening and provide ongoing monitoring throughout treatment. They often offer competitive pricing and convenient home delivery of medications.
Considerations for Prescription Access
Cost considerations vary significantly between providers and treatment options. Generic finasteride costs substantially less than brand-name versions, while minoxidil is available over-the-counter without prescription.
Insurance coverage for hair loss treatments remains limited, with most plans excluding cosmetic treatments. Men should verify coverage before beginning treatment to understand out-of-pocket expenses.
Treatment continuity represents a crucial factor in prescription planning. Since hair loss treatments for men require lifelong use to maintain benefits, establishing reliable prescription access is essential for long-term success.
FAQs About Treating Baldness in Men Effective Solutions Guide
What is male pattern baldness and its causes?
Male pattern baldness is a hereditary condition caused primarily by DHT hormone sensitivity, leading to progressive hair follicle miniaturization and eventual hair loss in predictable patterns.
What are some effective hair loss treatments?
The most effective hair loss treatments include FDA-approved medications finasteride and minoxidil, which can slow hair loss progression and promote regrowth in many men.
Who is a suitable candidate for treatment?
Men aged 18-65 with early to moderate male pattern baldness, good overall health, and realistic expectations represent ideal candidates for hair loss treatment.
What are the side effects of hair medication?
Common side effects of hair loss drugs include sexual dysfunction with finasteride (2-4% of users) and scalp irritation with minoxidil, though most men tolerate treatments well.
Follow us on social media for updates, tips, and patient success stories: