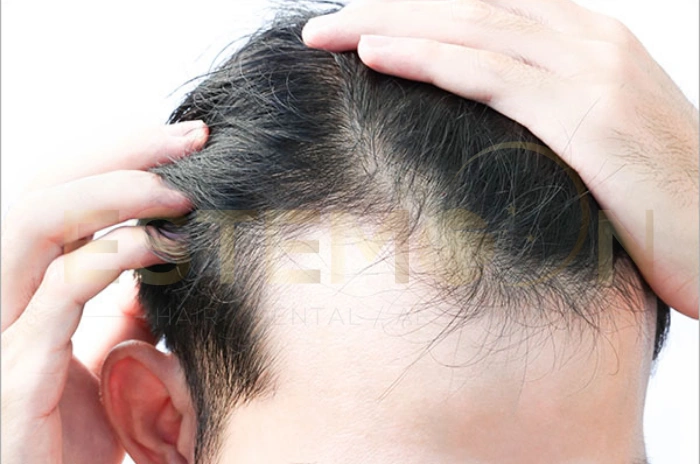
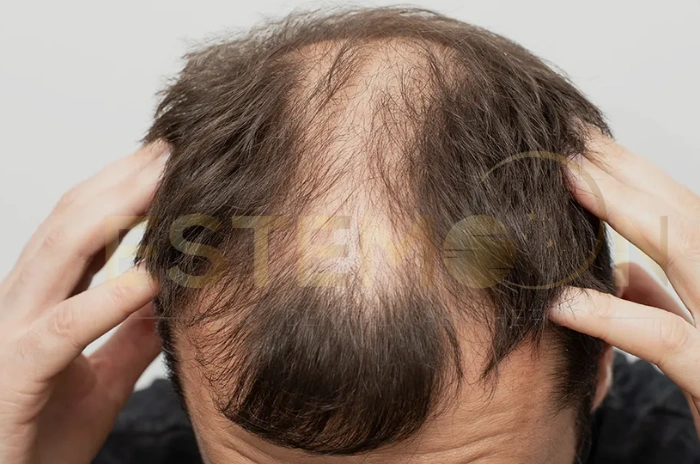
Telogen effluvium is one of the most common forms of diffuse hair loss that affects millions of people worldwide. This temporary but distressing condition causes widespread hair thinning and increased hair shedding, often leaving individuals concerned about permanent baldness. Understanding the nature of this nonscarring alopecia is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Unlike other forms of hair loss that create distinct bald patches, telogen effluvium presents as uniform thinning across the entire scalp. The condition occurs when a significant number of hair follicles prematurely enter the resting phase of the hair cycle, leading to increased shedding approximately three months later.
What is Telogen Effluvium
Telogen effluvium represents a disruption in the normal hair growth cycle, specifically affecting the telogen phase. In healthy individuals, approximately 10-15% of hair follicles remain in the resting telogen phase at any given time. However, in telogen effluvium, this percentage can increase dramatically to 30% or more.
The condition manifests as diffuse hair loss without creating specific bald areas. Instead, patients notice overall thinning and increased hair shedding during washing, brushing, or simply running fingers through their hair. The scalp typically remains healthy-looking without inflammation or scarring.
Acute telogen effluvium develops suddenly and usually resolves within six months once the triggering factor is addressed. In contrast, chronic telogen effluvium persists for longer periods, sometimes lasting several years, and may require more intensive management approaches.
Causes of Telogen Effluvium
The underlying causes of telogen effluvium are diverse and often interconnected. Physical stressors represent the most common triggers, including severe illness, major surgery, high fever, or significant weight loss. These events can shock the hair follicles into prematurely entering the telogen phase.
| Category | Common Triggers | Onset Timeline |
|---|---|---|
| Physical Stress | Surgery, fever, illness, rapid weight loss | 2-3 months delay |
| Hormonal Changes | Postpartum hair loss, thyroid disorders, menopause | 2-5 months delay |
| Nutritional Deficiencies | Iron deficiency hair loss, protein deficiency, crash dieting | 3-6 months delay |
| Medications | Beta blockers hair loss, retinoids vitamin A hair loss, anticoagulants | 1-4 months delay |
| Emotional Stress | Major life changes, work stress, relationship problems | 2-4 months delay |
Hormonal fluctuations frequently trigger diffuse hair loss. Postpartum hair loss affects up to 90% of new mothers, occurring 2-5 months after delivery when estrogen levels drop dramatically. Hypothyroidism hair loss can disrupt the normal hair cycle and lead to persistent shedding.
Symptoms and Signs of Hair Shedding
The primary symptom of telogen effluvium is increased hair shedding that typically becomes noticeable 2-3 months after the triggering event. Patients often report losing 100-300 hairs daily, significantly more than the normal 50-100 hairs per day.
Diffuse hair loss creates uniform thinning across the entire scalp rather than concentrated areas of baldness. The hairline typically remains intact, helping distinguish this condition from female pattern hair loss or male pattern hair loss. The hair pull test serves as a simple diagnostic tool that dermatologists use to assess shedding.

Who gets telogen effluvium
Telogen effluvium affects people of all ages, genders, and ethnicities, though certain populations show higher susceptibility. Women experience this condition more frequently than men, particularly during reproductive years when hormonal fluctuations are common. Postpartum hair loss represents the most frequent form of acute telogen effluvium in women.
Individuals with underlying health conditions face increased risk. Those with thyroid disorders, autoimmune conditions, or chronic illnesses are more prone to developing chronic telogen effluvium. Age plays a role in susceptibility, with middle-aged adults more commonly affected due to accumulated stress factors.
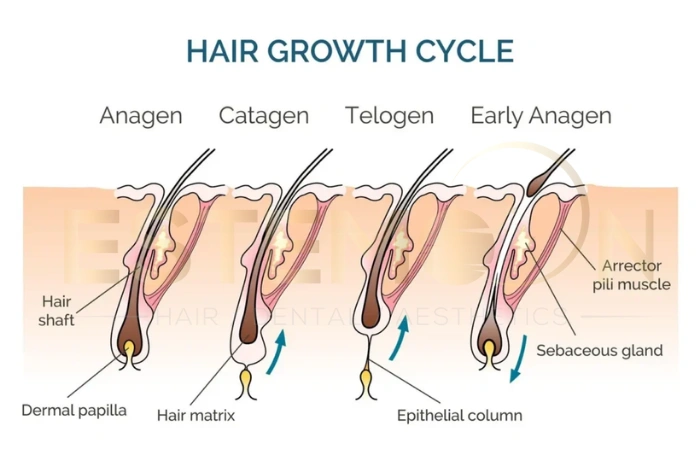
How the hair cycle changes in telogen effluvium
Understanding the normal hair cycle helps explain how telogen effluvium develops. The anagen phase represents the active growth period, lasting 2-7 years, during which hair follicles produce new hair fiber. This phase typically involves 85-90% of scalp hairs at any given time.
In telogen effluvium, triggering factors cause a premature shift from anagen phase to telogen phase. This disruption affects a much larger percentage of hair follicles simultaneously, creating the characteristic diffuse hair loss pattern. Chronic telogen effluvium may involve repeated cycling disruptions or shortened anagen phases.
Telogen Effluvium Treatment and Management Options
Effective treatment of telogen effluvium begins with identifying and addressing underlying triggers. When nutritional deficiencies contribute to hair shedding, appropriate supplementation can promote recovery. Iron deficiency hair loss responds well to iron supplementation, though improvement may take 3-6 months.
Minoxidil for telogen effluvium represents the most commonly prescribed topical treatment. This FDA-approved medication can help stimulate hair regrowth and potentially reduce shedding duration. Both 2% and 5% concentrations are available, with the higher strength typically reserved for more severe cases.
Mesotherapy for hair loss involves injecting nutrient-rich solutions directly into the scalp. This treatment may help nourish hair follicles and potentially accelerate recovery. Addressing underlying medical conditions is essential for long-term success, including proper thyroid hormone replacement therapy for hypothyroidism hair loss.
Common triggers of telogen effluvium
Physical stressors represent the most frequent triggers of acute telogen effluvium. Major surgery, severe infections, high fevers, and significant weight loss can all shock hair follicles into premature resting phases. Psychological stress increasingly contributes to diffuse hair loss in modern society.
Dietary factors frequently precipitate telogen effluvium. Crash dieting, eating disorders, and malabsorption conditions can create nutritional deficiencies that disrupt the hair cycle. Beta blockers hair loss affects some cardiovascular patients, while retinoids vitamin A hair loss can result from both prescription medications and excessive supplementation.
Hormonal fluctuations create predictable patterns of hair loss. Postpartum hair loss affects the majority of new mothers, while menopause, thyroid disorders, and polycystic ovary syndrome can all trigger chronic telogen effluvium. Birth control pill changes may also precipitate shedding episodes.
FAQs About Telogen Effluvium Guide to Causes Symptoms and Treatment
Can telogen effluvium be a chronic condition?
Yes, chronic telogen effluvium can persist for months or even years, particularly when underlying triggers remain unaddressed or when multiple factors contribute to ongoing hair shedding.
How does diet impact telogen effluvium recovery?
A balanced diet rich in protein, iron, vitamins, and minerals is essential for hair regrowth, as nutritional deficiencies can prolong diffuse hair loss and delay recovery from telogen effluvium.
What is the timeline for hair regrowth?
Most patients with acute telogen effluvium see improvement within 6-12 months after addressing triggers, though full hair density recovery may take up to 18 months.
Should I see a doctor for this condition?
Yes, consulting a dermatologist is recommended for persistent hair shedding to rule out other conditions like female pattern hair loss, diffuse alopecia areata, or underlying medical issues requiring treatment.
Follow us on social media for updates, tips, and patient success stories: