Hair loss concerns affect millions of people worldwide, and understanding the difference between normal hair shedding and problematic hair loss is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment. The hair pull test is one of the most important diagnostic tools that dermatologists and trichologists use to evaluate hair shedding patterns and determine whether your hair loss falls within normal parameters.
This simple yet effective examination technique helps medical professionals assess the health of your hair follicles and identify various types of alopecia. Whether you’re experiencing sudden hair thinning, increased shedding, or patchy hair loss, understanding what a hair pull test involves can help you better communicate with your healthcare provider and make informed decisions about your hair health.
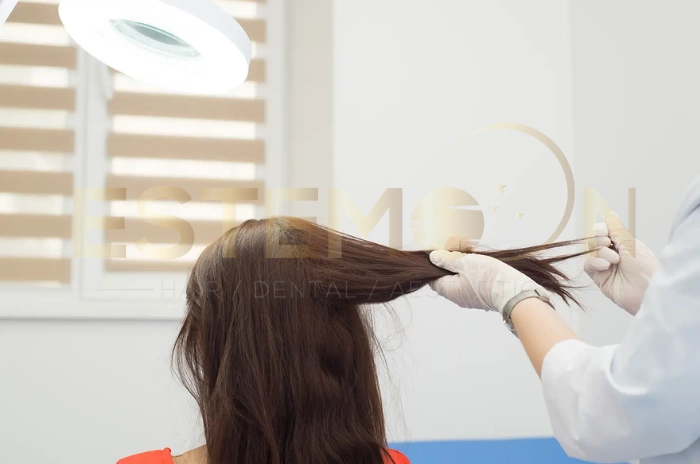

What Is a Hair Pull Test?
A hair pull test is a diagnostic procedure performed by healthcare professionals to evaluate hair shedding and assess the overall health of hair follicles. During this examination, a doctor gently grasps approximately 50-60 hairs between their thumb and index finger, then pulls with steady, moderate pressure from the scalp to the hair tips.
The test is typically performed on different areas of the scalp, including the frontal, temporal, and occipital regions. This comprehensive approach ensures that any localized hair loss patterns are properly identified. The procedure is generally painless and takes only a few minutes to complete.
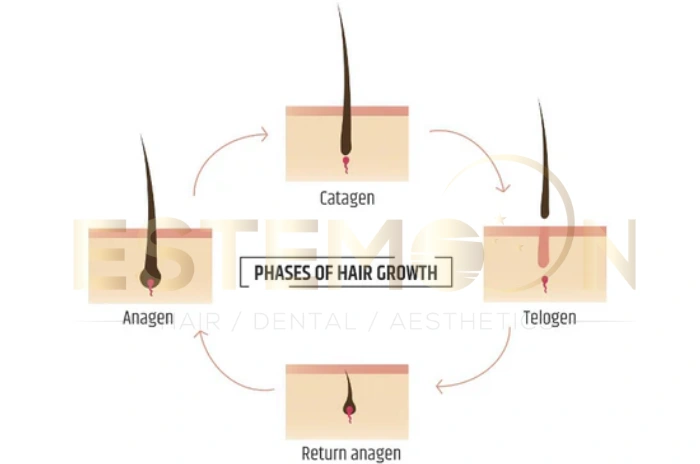
Medical professionals count the number of hairs that come out during each pull and examine them under magnification to determine their growth phase. The hair pull test provides valuable information about whether hair follicles are functioning normally or if there’s an underlying condition affecting hair growth cycles.
The simplicity of this test makes it an excellent first-line diagnostic tool for hair loss evaluation. Unlike more invasive procedures, the hair pull test can be performed during a routine office visit without requiring special equipment or preparation from the patient.
When the Hair Pull Test is Helpful for Shedding Problems
The hair pull test is particularly valuable when patients report increased hair shedding or notice more hair in their brush, shower drain, or on their pillow. This diagnostic tool helps differentiate between normal daily hair loss and pathological hair shedding that requires medical intervention.
Healthcare providers often recommend a hair pull test when patients experience sudden onset hair loss, diffuse thinning across the scalp, or when there’s uncertainty about whether observed hair loss exceeds normal parameters. The test is especially useful for diagnosing telogen effluvium, a common condition characterized by excessive shedding due to stress, illness, or hormonal changes.
Patients who have undergone significant life events such as surgery, childbirth, severe illness, or major dietary changes may benefit from this evaluation. The hair pull test can help determine if these events have triggered abnormal hair shedding patterns and guide appropriate treatment decisions.
The test is also valuable for monitoring treatment progress in patients already diagnosed with hair loss conditions. Regular hair pull test evaluations can help doctors assess whether treatments are effectively reducing excessive shedding and promoting healthier hair growth cycles.
Why Do Doctors Perform a Hair Pull Test?
Medical professionals perform a hair pull test to obtain objective data about hair shedding patterns and follicle health. This diagnostic tool provides immediate, quantifiable results that help doctors distinguish between various types of hair loss conditions and determine the most appropriate treatment approach.
The test helps identify whether hair loss is due to increased shedding from existing follicles or actual follicle damage and destruction. This distinction is crucial because different types of hair loss require different treatment strategies and have varying prognoses for recovery.
Doctors also use the hair pull test to assess the severity of hair loss conditions and monitor disease progression over time. By performing the test during follow-up visits, healthcare providers can evaluate treatment effectiveness and make necessary adjustments to therapeutic plans.
The procedure is particularly valuable for diagnosing telogen effluvium, anagen effluvium, and certain types of alopecia areata. The hair pull test results, combined with patient history and physical examination findings, provide a comprehensive picture of the underlying hair loss condition.
Normal vs. Abnormal Hair Pull Test Results
Understanding normal hair pull test results is essential for both patients and healthcare providers. In a healthy individual, fewer than 3 hairs should come out when the test is performed correctly. This represents the normal daily shedding that occurs as part of the natural hair growth cycle.
When 4-6 hairs are extracted during the test, results are considered borderline, and additional evaluation may be necessary to determine if there’s an underlying problem. Healthcare providers typically consider patient history, recent life events, and other clinical findings when interpreting borderline results.
Abnormal hair pull test results occur when more than 6 hairs are extracted during the procedure. This indicates excessive shedding and suggests the presence of a hair loss condition requiring medical attention. The higher the number of extracted hairs, the more severe the shedding problem.
A positive hair pull test meaning refers to abnormal results where excessive hair shedding is demonstrated. These results often indicate conditions such as telogen effluvium, nutritional deficiencies, hormonal imbalances, or other systemic conditions affecting hair growth. Prompt evaluation and treatment are typically recommended when positive results are obtained.
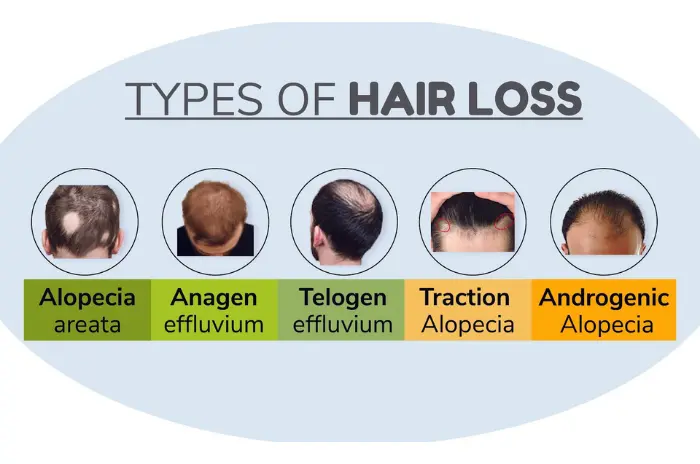
What Causes Excessive Hair Shedding?
Excessive hair shedding can result from numerous factors that disrupt the normal hair growth cycle. Telogen effluvium is one of the most common causes, typically triggered by physical or emotional stress, hormonal changes, nutritional deficiencies, or medications that push hair follicles into the resting phase prematurely.
Hormonal fluctuations, particularly those related to thyroid disorders, pregnancy, menopause, or androgen imbalances, can significantly impact hair growth cycles. These hormonal changes can cause widespread hair thinning and increased shedding that would be detected through a hair pull test.
Nutritional deficiencies, especially iron deficiency, vitamin D deficiency, and inadequate protein intake, are frequent culprits in excessive hair shedding. The body prioritizes essential functions over hair growth during periods of nutritional stress, leading to increased hair loss that can persist for months.
Medications such as blood thinners, antidepressants, birth control pills, and chemotherapy drugs can cause anagen effluvium causes or telogen effluvium. Understanding medication-related hair loss is crucial for proper diagnosis and management of shedding problems.
Autoimmune conditions, severe illnesses, surgical procedures, and extreme weight loss can also trigger excessive hair shedding. These stressors can shift large numbers of hair follicles into the telogen phase simultaneously, resulting in noticeable hair loss several months later.
Can a Hair Pull Test Diagnose Hair Loss?
While a hair pull test is an valuable diagnostic tool, it cannot definitively diagnose all types of hair loss conditions on its own. The test provides important information about hair shedding patterns, but comprehensive hair loss diagnosis requires correlation with patient history, physical examination, and often additional testing.
For conditions like telogen effluvium, the hair pull test is highly sensitive and can effectively identify excessive shedding. However, for androgenetic alopecia or scarring alopecias, additional evaluation methods such as dermoscopy, scalp biopsy for hair loss, or specialized imaging may be necessary.
Hair loss diagnosis tests often include blood work to evaluate thyroid function, iron levels, vitamin D status, and hormonal parameters. These laboratory studies complement the hair pull test results and help identify underlying systemic causes of hair loss.
The best hair loss tests at home are limited, but patients can perform a modified version of the hair pull test to monitor their shedding patterns. However, professional evaluation remains essential for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment planning.
Some dermatologists may recommend additional procedures such as scalp biopsy for hair loss when the diagnosis remains unclear or when scarring alopecia is suspected. These more invasive tests provide detailed information about follicle structure and inflammatory processes that cannot be assessed through a simple hair pull test.
Understanding hair shedding vs hair loss is crucial for proper evaluation. Hair shedding refers to the natural daily loss of hair, while hair loss implies a reduction in overall hair density due to decreased hair production or follicle damage.
FAQs About Hair Pull Test: Everything You Need To Know
What is a hair pull test for?
A hair pull test is used to evaluate excessive hair shedding and assess the health of hair follicles by gently pulling a small section of hair to count how many strands come out.
Can a doctor perform a hair pull test?
Yes, dermatologists and other healthcare providers routinely perform hair pull tests as part of comprehensive hair loss evaluations in clinical settings.
What are normal results for a hair pull test?
Normal hair pull test results show fewer than 3 hairs extracted when the test is performed correctly on healthy individuals.
Does a hair pull test diagnose hair loss?
A hair pull test helps identify excessive shedding but cannot diagnose all types of hair loss conditions without additional clinical evaluation and testing.