Genetic hair loss, also known as androgenetic alopecia, is a common condition that affects millions of men and women worldwide. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and available treatments can help you manage and even reverse hair loss. This comprehensive guide will provide you with all the essential information about genetic hair loss.
What is Genetic Hair Loss?
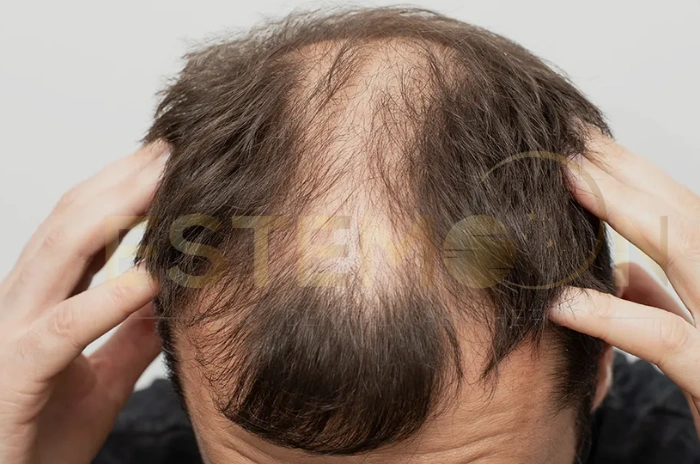
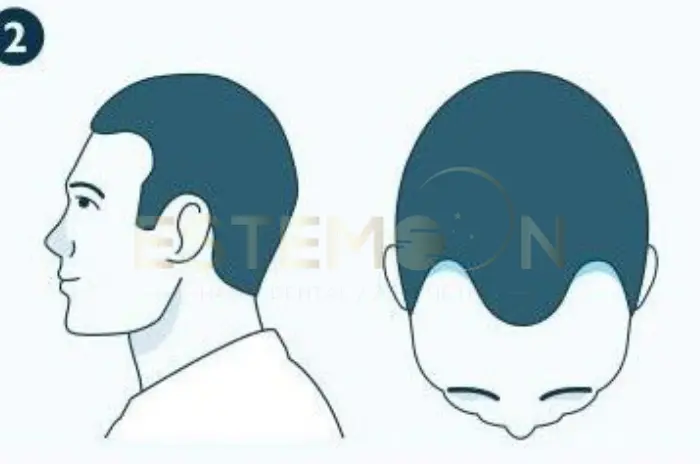
Genetic hair loss is a hereditary condition that leads to the gradual thinning and loss of hair. It is most commonly observed in men as male pattern baldness, but it also affects women, known as female pattern baldness. This type of hair loss is caused by a combination of genetics, hormones, and age.
Causes of Genetic Hair Loss
The primary cause of genetic hair loss is the presence of certain genes inherited from one or both parents. These genes make hair follicles sensitive to dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone derived from testosterone. DHT binds to receptors in the hair follicles, causing them to shrink and eventually stop producing hair. Other contributing factors include:
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations, particularly in men, can accelerate hair loss.
- Age: The likelihood of experiencing genetic hair loss increases with age.
- Family History: A family history of baldness significantly increases the risk of developing genetic hair loss.
Symptoms of Genetic Hair Loss
The symptoms of genetic hair loss vary between men and women:
In Men:
- Receding hairline, especially at the temples
- Thinning hair on the crown
- A noticeable bald spot
In Women:
- Overall thinning of hair
- Widening of the part line
- Thinning hair primarily at the crown
Diagnosis of Genetic Hair Loss
A dermatologist or hair specialist can diagnose genetic hair loss through a physical examination and by reviewing your medical and family history. In some cases, a scalp biopsy or blood tests may be conducted to rule out other causes of hair loss.
Treatment Options for Hair Loss
While there is no cure for genetic hair loss, several effective treatments can slow down or even reverse the process:
- Medications:
- Minoxidil (Rogaine): An over-the-counter topical treatment that stimulates hair growth.
- Finasteride (Propecia): A prescription oral medication that reduces DHT levels.
- Hair Transplant Surgery: This surgical procedure involves moving hair follicles from a donor area to the balding areas.
- Laser Therapy: Low-level laser therapy (LLLT) can stimulate hair growth and increase hair density.
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy: PRP injections can promote hair growth by using your blood’s growth factors.
- Lifestyle Changes: Maintaining a healthy diet, reducing stress, and using gentle hair care products can support overall hair health.
Coping with Hair Loss
Dealing with genetic hair loss can be emotionally challenging. Consider joining support groups or seeking counseling to manage the psychological impact. Additionally, exploring cosmetic options such as wigs, hairpieces, or scalp micropigmentation can help improve your appearance and boost your confidence.
Genetic hair loss is a common but manageable condition. By understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options, you can take proactive steps to address hair loss and maintain a healthy head of hair. Consult with a hair specialist to determine the best treatment plan for your specific needs and start your journey towards regaining confidence and a fuller head of hair.