Finasteride has become one of the most widely prescribed treatments for male pattern baldness, offering hope for millions of men experiencing hair loss. At Estemoon intermediary organization, we help patients understand realistic expectations and track progress throughout their finasteride journey with comprehensive monitoring and expert guidance.
What Finasteride Is and How It Helps Hair Loss
Finasteride is an FDA-approved oral medication specifically designed to treat male pattern baldness (androgenetic alopecia). Originally developed in the 1990s for treating enlarged prostate glands, researchers discovered its remarkable hair restoration properties during clinical trials when patients reported unexpected hair regrowth as a side effect.
The Science Behind Finasteride: Finasteride belongs to a class of medications called 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors. This enzyme is responsible for converting testosterone into dihydrotestosterone (DHT), the primary hormone that causes hair follicle miniaturization and eventual hair loss in genetically susceptible men.
How DHT Affects Hair Follicles:
- DHT binds to androgen receptors in hair follicles
- This binding triggers a progressive shrinking process called miniaturization
- Hair strands become progressively thinner and weaker over time
- Eventually, follicles stop producing visible hair altogether
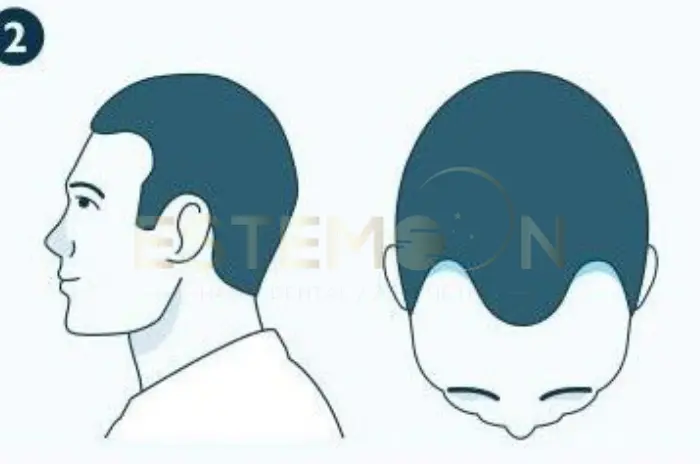
- The process typically follows a predictable pattern starting at the temples and crown
Finasteride’s Protective Mechanism: By blocking approximately 70% of DHT production, finasteride creates a more favorable environment for hair follicles to function normally. This reduction allows miniaturized follicles to gradually recover their original size and begin producing thicker, healthier hair strands.
| DHT Reduction Timeline | Percentage Decrease | Hair Follicle Response |
|---|---|---|
| 24 hours | 65% | Initial protection begins |
| 2 weeks | 70% | Miniaturization slows |
| 3 months | 70% maintained | Follicle recovery starts |
| 6+ months | 70% maintained | Visible improvement begins |
Finasteride Results Timeline Month by Month
Understanding the finasteride timeline helps patients maintain realistic expectations and stay committed to treatment during the initial phases when results may not be immediately visible.
Months 1-3: Initial Phase During the first three months, patients typically don’t see significant visual improvements. This period often involves initial hair shedding as weak, miniaturized hairs are replaced by stronger ones. The medication begins blocking DHT (dihydrotestosterone) production, but visible changes require time.
- Week 1-4: No visible changes expected, possible initial shedding
- Week 5-8: Continued stabilization, reduced daily hair loss may be noticed
- Week 9-12: Some patients report less hair in shower drain or on pillowcase
Months 4-6: Early Progress Phase The second quarter often brings the first encouraging signs of treatment effectiveness. Hair loss typically slows significantly, and some patients begin noticing subtle improvements in hair density.
- Month 4: Noticeable reduction in active hair loss
- Month 5: Possible early signs of new hair growth in affected areas
- Month 6: Stabilization of hair loss, potential minor density improvements
Months 7-12: Visible Improvement Phase This period typically shows the most dramatic improvements for responsive patients. Hair density increases become more apparent, and photography comparisons reveal clear progress.
| Time Period | Expected Changes | Hair Loss Status | New Growth | Patient Satisfaction |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Months 1-3 | Minimal visible change | May increase initially | None to minimal | Low |
| Months 4-6 | Stabilization | Significantly reduced | Early signs | Moderate |
| Months 7-12 | Visible improvement | Greatly reduced | Noticeable | High |
| Year 2+ | Peak results | Minimal | Maximized | Very High |
Individual variation factors:
- Age at treatment initiation affects response speed
- Baseline hair loss severity influences timeline
- Genetic factors determine individual responsiveness
- Consistency of daily medication adherence impacts results
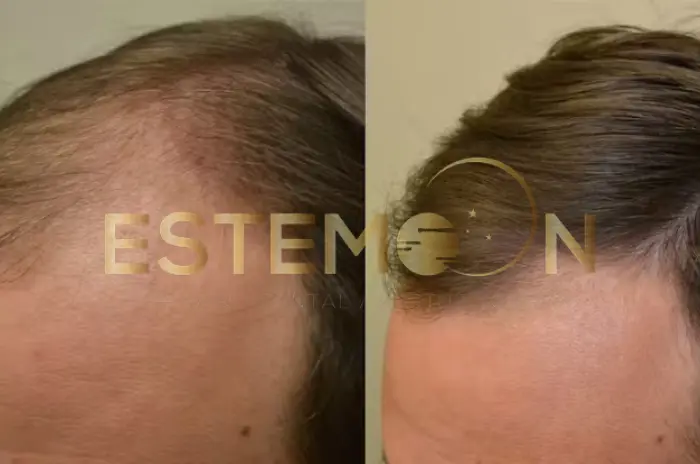
Finasteride Before and After Photos
Before and after photography serves as the most objective method for tracking finasteride progress, providing visual evidence of treatment effectiveness over time.
Professional photography standards:
- Consistent lighting: Use same location and lighting conditions for all photos
- Standardized angles: Front view, crown view, and both side profiles
- Hair preparation: Clean, dry hair styled consistently for each session
- Background consistency: Plain background without distracting elements
- Documentation frequency: Monthly photos for first year, then quarterly
Key photographic considerations: Professional intermediary organizations often use specialized photography equipment with standardized lighting to ensure accurate comparison. Patients taking home photos should maintain consistency in timing, location, and hair preparation to achieve meaningful comparisons.
Photo timing recommendations:
- Baseline photos before starting treatment
- Monthly documentation during first six months
- Quarterly photos after achieving stability
- Annual comprehensive photo sessions for long-term tracking
Common photography mistakes:
- Inconsistent lighting creating false impressions of improvement or decline
- Different hair lengths affecting density appearance
- Varying camera angles making comparison difficult
- Wet versus dry hair inconsistency
What to Look for in Finasteride Photos
Analyzing finasteride progress photos requires understanding specific visual indicators that demonstrate treatment effectiveness and hair restoration progress.
Density improvements:
- Scalp visibility reduction: Less scalp showing through hair coverage
- Hair thickness increase: Individual hair strands appearing thicker and stronger
- Coverage expansion: Previously bald areas showing new hair growth
- Overall fullness: General improvement in hair volume and appearance
Hairline assessment:
- Edge definition: Sharper, more defined hairline borders
- Miniaturized hair recovery: Weak hairs becoming terminal hairs
- Recession halt: Prevention of further hairline retreat
- Temple area improvements: Specific attention to temporal recession areas
Crown and vertex evaluation:
- Central scalp coverage: Reduced visibility of scalp at the crown
- Whorl area improvement: Better hair coverage around the natural whorl
- Diffuse thinning reversal: Overall density improvement across affected areas
Quality indicators to monitor:
- Hair strand diameter and strength improvements
- Natural shine and healthy appearance
- Reduced brittleness and breakage
- Improved styling capability and hold
Results Before One Year What to Expect
The first year of finasteride treatment involves several distinct phases, each with specific expectations and potential challenges that patients should understand.
Months 1-6: Foundation Period The initial six months focus primarily on stabilizing hair loss rather than achieving dramatic regrowth. Patients should expect gradual improvements rather than immediate transformation.
Expected outcomes:
- Hair loss reduction: 80-90% decrease in daily hair shedding
- Stabilization: Halting or significantly slowing further hair loss
- Quality improvements: Existing hair may become stronger and healthier
- Minimal regrowth: Limited new hair growth in most patients
Months 7-12: Growth and Improvement Phase The second half of the first year typically brings more visible improvements, with many patients experiencing their most significant progress during this period.
Realistic expectations:
- Density increase: 10-15% improvement in overall hair density
- Coverage improvement: Better scalp coverage in affected areas
- Hair quality enhancement: Thicker, stronger individual hair strands
- Styling improvements: Easier styling and better hair hold
Managing expectations: Not all patients respond equally to finasteride treatment. Approximately 80-85% of patients experience stabilization of hair loss, while 60-65% see some degree of regrowth. Understanding these statistics helps maintain realistic expectations and treatment satisfaction.
Who Can Use Finasteride for Hair Loss
Finasteride is specifically approved for men aged 18 and older experiencing male pattern baldness. However, not all men are suitable candidates for this treatment, making proper evaluation essential.
Ideal Candidates for Finasteride:
| Criteria | Details | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Age Range | 18-65 years old | High |
| Hair Loss Type | Male pattern baldness only | Critical |
| Health Status | Good overall health | Important |
| Expectations | Realistic treatment goals | Essential |
| Commitment | Long-term treatment adherence | Critical |
Medical Eligibility Requirements:
- Normal liver function test results
- No history of prostate cancer or suspicious PSA levels
- Absence of severe depression or mood disorders
- No plans for immediate conception (temporary fertility effects)
- Understanding of treatment commitment and potential side effects
Exclusions and Contraindications:
- Women: Finasteride is strictly contraindicated in women, especially those of childbearing age
- Children: Not approved for use in individuals under 18 years
- Liver Disease: Impaired liver function affects medication metabolism
- Prostate Issues: History of prostate cancer or elevated PSA levels
- Allergic Reactions: Previous hypersensitivity to finasteride or related compounds
Special Populations: Men over 65 can use finasteride, but they require more frequent monitoring due to increased prostate cancer risk with age. Regular PSA testing becomes particularly important in this demographic.
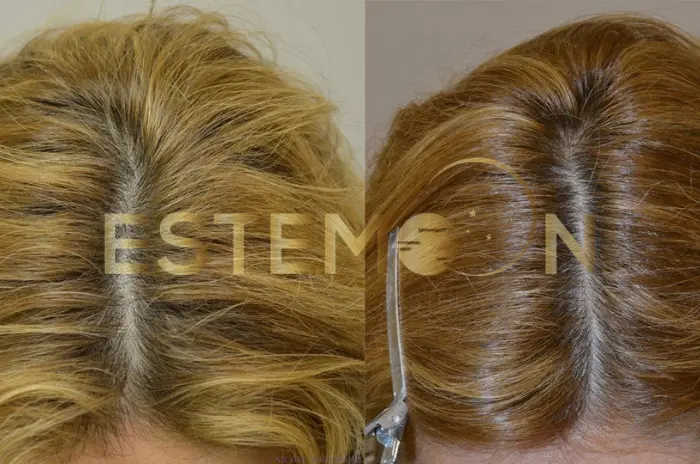
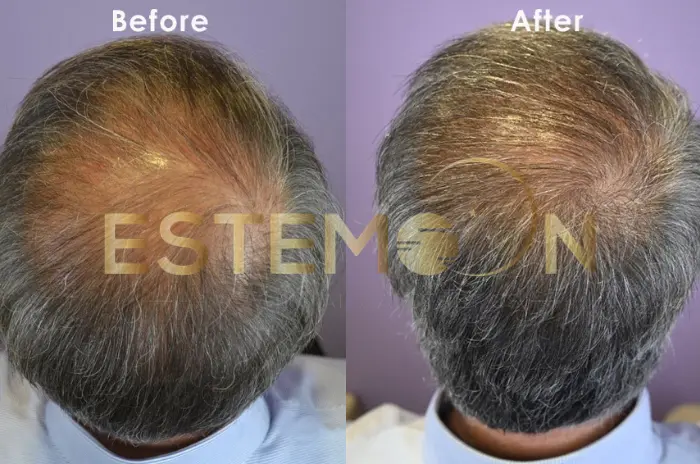
One Year Finasteride Results and Progress
The one-year mark represents a crucial milestone in finasteride treatment, providing the clearest picture of individual treatment response and long-term prognosis.
Typical one-year outcomes:
- Stabilization success: Most patients achieve significant hair loss reduction
- Regrowth achievement: Moderate to significant improvement in 60-65% of patients
- Quality improvements: Enhanced hair strength, thickness, and manageability
- Psychological benefits: Improved confidence and reduced anxiety about hair loss
Categories of response:
- Excellent responders (20-25%): Dramatic improvement with significant regrowth
- Good responders (35-40%): Moderate improvement with noticeable changes
- Stabilizers (20-25%): Maintenance of existing hair without significant loss
- Poor responders (10-15%): Minimal improvement or continued gradual loss
Assessment criteria at one year: Professional evaluation typically includes photographic comparison, hair count measurements, patient satisfaction surveys, and clinical assessment of hair quality and coverage improvements.
Next steps consideration: Based on one-year results, patients and healthcare providers can make informed decisions about continuing treatment, adjusting dosage, or considering additional therapies like minoxidil or hair transplantation.
Long Term Finasteride Results and Maintenance
Long-term finasteride use requires understanding maintenance expectations, potential changes over time, and strategies for optimizing continued effectiveness.
Years 2-5: Maintenance Phase After the initial year of improvement, most patients enter a maintenance phase where the primary goal shifts from achieving new growth to preserving gains and preventing further loss.
Long-term expectations:
- Sustained improvement: Maintenance of gains achieved in first year
- Gradual enhancement: Some patients continue seeing minor improvements
- Loss prevention: Continued protection against DHT-related hair loss
- Quality maintenance: Preservation of improved hair strength and thickness
Maintenance strategies:
- Consistent daily dosing: Maintaining regular medication schedule
- Regular monitoring: Periodic assessment with healthcare providers
- Lifestyle optimization: Supporting overall hair health through proper nutrition
- Combination approaches: Adding complementary treatments when appropriate
| Treatment Duration | Expected Outcomes | Maintenance Focus | Monitoring Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Year 1 | Initial improvement | Establishing response | Monthly |
| Years 2-3 | Peak benefits | Maintaining gains | Quarterly |
| Years 4-5 | Stable maintenance | Prevention focus | Bi-annually |
| Years 5+ | Continued protection | Long-term stability | Annually |
Long-term considerations:
- Age-related changes: Natural aging effects on hair quality
- Hormonal fluctuations: Impact of aging on treatment effectiveness
- Lifestyle factors: Diet, stress, and health changes affecting results
- Treatment adherence: Maintaining consistent use over decades
Finasteride as a Treatment for Male Pattern Baldness
Finasteride represents the gold standard oral treatment for androgenetic alopecia, offering scientifically proven effectiveness in treating male pattern baldness.
Mechanism of action:
- DHT inhibition: Blocks 5-alpha reductase enzyme, reducing DHT production by approximately 70%
- Follicle protection: Prevents DHT-mediated miniaturization of hair follicles
- Growth cycle normalization: Allows affected follicles to recover and produce terminal hairs
- Systemic effectiveness: Provides comprehensive scalp coverage through oral administration
Clinical effectiveness:
- Hair loss prevention: 80-90% of patients experience significant hair loss reduction
- Regrowth achievement: 60-65% of patients see measurable hair regrowth
- Long-term stability: Sustained benefits with continued use over multiple years
- Quality of life improvement: Enhanced self-confidence and reduced hair loss anxiety
Treatment candidacy: Ideal candidates include men with mild to moderate male pattern baldness who start treatment before extensive hair loss occurs. Early intervention typically provides better outcomes than treatment initiated after significant balding has already occurred.
Safety and monitoring: Regular follow-up with healthcare providers ensures optimal treatment outcomes while monitoring for potential side effects. Most patients tolerate finasteride well with minimal adverse effects.
Combination therapy options: Many patients achieve enhanced results by combining finasteride with topical minoxidil, low-level laser therapy, or other complementary treatments under professional guidance from intermediary organizations.
Common Side Effects of Finasteride in Hair Loss Therapy
Understanding potential side effects helps patients make informed decisions and manage their treatment effectively. Most side effects are mild, temporary, and affect only a small percentage of users.
Documented Side Effect Frequencies:
| Side Effect | Frequency | Duration | Reversibility |
|---|---|---|---|
| Decreased libido | 1.8% | Temporary | Usually reversible |
| Erectile dysfunction | 1.3% | Temporary | Usually reversible |
| Ejaculation disorders | 1.2% | Temporary | Usually reversible |
| Breast tenderness | 0.4% | Variable | Usually reversible |
| Depression/mood changes | 0.2% | Variable | Requires monitoring |
Managing Side Effects: Most patients who experience side effects find they resolve within the first few months of treatment as the body adjusts to the medication. For those experiencing persistent issues, dose reduction or treatment holidays under medical supervision can help.
Rare but Serious Considerations:
- Post-finasteride syndrome: A controversial condition with persistent symptoms after discontinuation
- Breast changes: Rarely, men may develop breast lumps requiring evaluation
- Mood effects: Some patients report depression or anxiety, requiring careful monitoring
Patient Monitoring Protocol: Regular follow-up appointments allow healthcare providers to assess treatment response, monitor for side effects, and adjust therapy as needed. Open communication about any concerns ensures optimal treatment outcomes.
FAQ
What results can be expected after a year?
After one year of finasteride treatment, most patients can expect significant stabilization of hair loss with 80-90% reduction in daily hair shedding. Approximately 60-65% of patients experience measurable regrowth, ranging from modest density improvements to dramatic hair restoration. Hair quality typically improves with stronger, thicker strands and better styling capability. Results vary based on age, baseline hair loss severity, and individual response, with younger patients and those with less extensive loss generally achieving better outcomes.
Do you need to keep using finasteride forever?
Yes, finasteride requires continuous use to maintain benefits. The medication blocks DHT production only while being taken, so stopping treatment results in gradual return to pre-treatment hair loss patterns within 6-12 months. Long-term use is generally safe and well-tolerated, with most patients continuing treatment for years or decades. Regular monitoring with healthcare providers ensures ongoing safety and effectiveness while adjusting treatment as needed based on individual response and goals.
How soon can you see finasteride results?
Initial finasteride results typically become noticeable after 4-6 months of consistent daily use. The first 3 months often show minimal visible change and may include temporary increased shedding. Significant improvements usually appear between months 6-12, with peak results achieved around 12-18 months. Early signs include reduced hair loss in shower or on pillowcase, followed by gradual density improvements. Patience is essential as hair growth cycles require time to respond to treatment.
What should I look for in photos?
In finasteride progress photos, look for reduced scalp visibility through hair coverage, improved hairline definition, and increased overall density. Key indicators include thicker individual hair strands, better coverage in previously thinning areas, and reduced miniaturized hairs along the hairline. Compare photos taken under consistent lighting conditions and hair preparation. Focus on overall coverage improvements rather than individual hair counts, and document changes in hair quality, shine, and styling capability alongside density improvements.
Follow us on social media for updates, tips, and patient success stories: