Discovering bumps on scalp can be concerning and uncomfortable. These raised areas on your head can range from small, painless bumps to larger, inflamed lesions that cause significant discomfort. Understanding the various causes of scalp bumps is crucial for proper treatment and prevention.
Scalp bumps affect millions of people worldwide and can result from numerous conditions including infections, inflammatory disorders, and even serious conditions like skin cancer. The scalp’s unique environment, with its dense hair follicles and sebaceous glands, creates specific conditions that can lead to various types of bumps and lesions.
Most bumps on scalp are benign and treatable, but some require immediate medical attention. Learning to identify different types of scalp bumps, their symptoms, and appropriate treatments can help you maintain healthy scalp skin and prevent complications.
Common Causes of Bumps on the Scalp
Sebaceous Cysts and Pilar Cysts
Scalp cysts are among the most common causes of bumps on the head. Pilar cysts specifically occur on the scalp and contain keratin, a protein found in hair and skin. These cysts typically feel firm, round, and can range from small pea-sized bumps to larger growths several centimeters in diameter.
Sebaceous cysts develop when hair follicles become blocked with oil and dead skin cells. Unlike other scalp bumps, these cysts are usually painless unless they become infected or inflamed.
Scalp Infections
Scalp infection can manifest as various types of bumps, including bacterial, fungal, and viral infections. Bacterial infections often result in painful, pus-filled bumps that may be accompanied by fever and swollen lymph nodes.
Viral infections like herpes zoster (shingles) can cause clusters of small, painful bumps along nerve pathways on the scalp. These infections require prompt medical treatment to prevent complications and reduce transmission risk.
Inflammatory Skin Conditions
Several inflammatory conditions can cause itchy scalp bumps and persistent discomfort. Contact dermatitis occurs when the scalp reacts to allergens or irritants in hair products, creating raised, red bumps that may ooze or crust over.
Autoimmune conditions can also trigger inflammatory responses that result in scalp bumps. These conditions often require specialized treatment and ongoing management to control symptoms effectively.
Effective Treatments for Scalp Bumps
Medical Treatments
Treatment for bumps on scalp depends on the underlying cause and severity of symptoms. Topical antibiotics are commonly prescribed for bacterial scalp infections, while antifungal medications treat fungal conditions like scalp ringworm.
For inflammatory conditions, dermatologists may prescribe topical or oral corticosteroids to reduce inflammation and itching. Severe cases might require immunosuppressive medications or biologic treatments.
| Treatment Type | Condition | Duration | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|---|
| Topical Antibiotics | Bacterial Folliculitis | 7-14 days | High |
| Antifungal Cream | Ringworm | 2-6 weeks | High |
| Corticosteroids | Eczema/Dermatitis | 1-4 weeks | Moderate-High |
| Oral Antibiotics | Severe Infections | 7-21 days | High |
Home Care Remedies
Gentle home care can support medical treatment and prevent scalp bumps from worsening. Use lukewarm water when washing hair and avoid harsh scrubbing that can irritate existing bumps.
Tea tree oil, when properly diluted, has antimicrobial properties that may help with minor scalp acne and folliculitis. However, essential oils should be patch-tested first and never used undiluted on the scalp.
Maintaining good scalp hygiene involves regular washing with gentle, sulfate-free shampoos. Avoid sharing hair tools, hats, or pillowcases that could spread infections or irritate sensitive scalp skin.
Eczema and Bumps on Scalp
Understanding Scalp Eczema
Scalp eczema, also known as seborrheic dermatitis, creates characteristic bumps and flaky patches on the scalp. This condition affects areas rich in sebaceous glands and can cause intense itching and inflammation.
Seborrheic dermatitis scalp symptoms include red, scaly patches that may appear greasy or crusty. The condition often worsens during stress, hormonal changes, or exposure to certain weather conditions.
Treatment and Management
Managing scalp eczema requires consistent care and appropriate medication. Medicated shampoos containing ketoconazole, selenium sulfide, or zinc pyrithione can help control fungal overgrowth that contributes to the condition.
Moisturizing the scalp with gentle, fragrance-free products helps maintain the skin barrier. Avoiding harsh chemicals, excessive heat styling, and tight hairstyles can prevent flare-ups and reduce irritation.
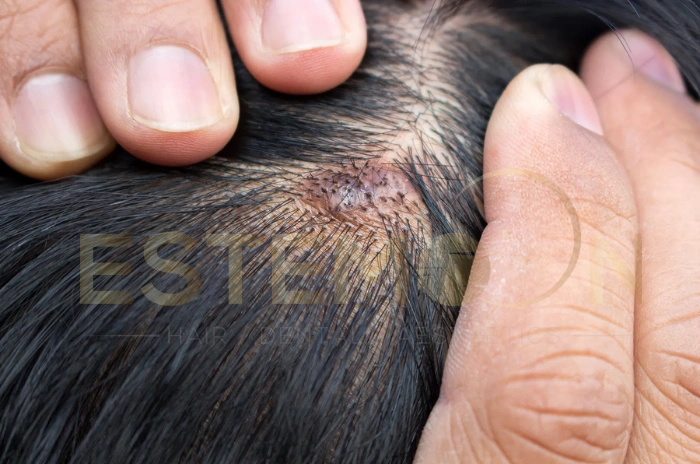
Why You Get Pimples on Your Scalp
Causes of Scalp Acne
Scalp acne develops when hair follicles become clogged with excess oil, dead skin cells, and bacteria. The scalp produces more sebum than other body areas, creating an environment conducive to acne development.
Hormonal fluctuations, particularly during puberty, menstruation, or pregnancy, can increase oil production and trigger scalp acne. Certain hair products containing heavy oils or comedogenic ingredients can also contribute to follicle blockage.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing scalp acne involves maintaining proper scalp hygiene without over-washing, which can stimulate more oil production. Wash hair regularly with non-comedogenic shampoos and avoid applying conditioner directly to the scalp.
Choose hair products labeled “non-comedogenic” or “oil-free” to reduce the risk of clogged follicles. Regular washing of pillowcases, hats, and hair accessories helps prevent bacterial buildup that can worsen scalp acne.
Head Lice and Bumps on the Scalp
Identifying Lice-Related Bumps
Head lice infestations can cause small, itchy bumps on the scalp, particularly around the hairline and behind the ears. These bumps result from allergic reactions to lice saliva and can become infected from excessive scratching.
Unlike other scalp bumps, lice-related bumps are accompanied by visible nits (lice eggs) attached to hair shafts near the scalp. Adult lice may also be visible as small, moving insects in the hair.
Treatment Approaches
Treating head lice requires specialized pediculicides (lice-killing medications) available over-the-counter or by prescription. Treatment typically involves applying medication to dry hair, leaving it for the specified time, then combing out dead lice and nits.
Secondary bacterial infections from scratching lice bumps may require antibiotic treatment. All household members should be checked for lice, and personal items like combs, brushes, and bedding should be cleaned thoroughly.
Folliculitis and Pimple-Like Scalp Bumps
Understanding Scalp Folliculitis
Scalp folliculitis occurs when hair follicles become infected with bacteria, fungi, or other pathogens. This condition creates pimple-like bumps that may be filled with pus and surrounded by red, inflamed skin.
Folliculitis can be acute (short-term) or chronic (long-lasting), depending on the underlying cause and individual factors. Chronic scalp folliculitis may lead to scarring and permanent hair loss if left untreated.
Risk Factors and Prevention
Several factors increase the risk of developing scalp folliculitis, including tight hairstyles, excessive sweating, and compromised immune function. Using contaminated hair tools or visiting poorly sanitized salons can also introduce infectious organisms.
Prevention involves keeping the scalp clean and dry, avoiding tight hairstyles that pull on hair follicles, and using clean hair tools. People with diabetes, HIV, or other immune-compromising conditions should be particularly vigilant about scalp hygiene.
Advanced Treatment Options
Severe or recurrent folliculitis may require oral antibiotics, antifungal medications, or even minor surgical procedures to drain infected follicles. Laser hair removal might be recommended for chronic cases to reduce hair follicle density and prevent future infections.
Photodynamic therapy and other advanced dermatological treatments show promise for treating resistant scalp folliculitis. These treatments should only be performed by qualified dermatologists or other medical professionals.
FAQs About Why You Have a Bump on Scalp Signs and Care
What are the most common causes of bumps on the scalp?
The most common causes include folliculitis, scalp acne, sebaceous cysts, seborrheic dermatitis scalp, and contact dermatitis from hair products.
How do I treat different kinds of stubborn scalp bumps?
Treatment depends on the cause but may include medicated shampoos, topical antibiotics, antifungal creams, or oral medications prescribed by a dermatologist.
Are pimple-like scalp bumps actually folliculitis?
Many pimple-like scalp bumps are indeed folliculitis, which occurs when hair follicles become infected with bacteria or other pathogens.
Do head lice and eczema also cause scalp bumps?
Yes, both head lice and scalp eczema can cause bumps – lice create itchy bumps from allergic reactions, while eczema causes inflamed, scaly bumps.
Follow us on social media for updates, tips, and patient success stories: