At Estemoon intermediary organization, we often see that hair loss is not only a biological condition but also a psychosocial one. Anxiety, chronic stress, and significant life events can disrupt the hair growth cycle, leading to telogen effluvium (sudden diffuse shedding), trichotillomania (hair pulling), and even accelerated androgenetic alopecia. This guide explains the relationship between stress and hair health, the types of stress-related hair loss, available treatment options, and practical daily management strategies.

Can Stress Cause Hair Loss?
Stress can result from illness, surgery, infection, emotional trauma, sleep deprivation, intense work demands, exam periods, or rapid weight loss. These triggers can shorten the hair’s growth phase (anagen) and push follicles prematurely into the resting phase (telogen). The result is noticeable shedding that often appears 2–3 months after the trigger.
Summary:
Acute stress → delayed onset (2–3 months) of sudden diffuse shedding (telogen effluvium)
Chronic stress/anxiety → ongoing cycle disruption, prolonging shedding
Genetic predisposition → stress can unmask or accelerate existing androgenetic alopecia
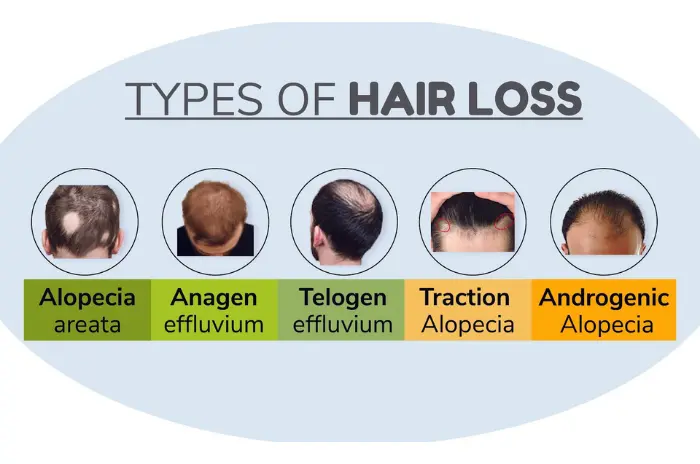
Types of Anxiety-Related Hair Loss
| Type | Mechanism | Clinical Appearance | Timing | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Telogen Effluvium (TE) | Stress/illness/surgery/weight loss → follicles enter telogen early | Diffuse thinning, handfuls of shedding hair | 2–3 months after trigger | Pull test shows telogen hairs; often reversible |
| Trichotillomania | Anxiety/tension → hair-pulling habit | Patchy, broken hairs of varying lengths | Ongoing | May also affect brows/lashes; behavioral cause |
| Androgenetic Alopecia (AGA) acceleration | Stress → inflammation/vascular changes accelerate pattern loss | Men: hairline/crown; Women: widening part | Over months | Miniaturization visible under dermoscopy |
| Alopecia Areata flare | Autoimmune response triggered by stress | Round patches of hair loss | Sudden | Dermoscopy may show “exclamation mark hairs” |
Note: More than one mechanism can be present in the same individual.
The Connection Between Anxiety and Hair Loss
Hair follicles are influenced by a network of nerve, immune, and hormonal signals. Anxiety and chronic stress can:
Increase cortisol and catecholamines, shortening anagen phase
Promote micro-inflammation and oxidative stress in the follicular environment
Disrupt sleep, nutrition, and daily routines essential for healthy hair
Lead to damaging behaviors such as tight hairstyles, excessive heat or chemical use, scalp scratching, or hair pulling
This means anxiety impacts hair through both biological and behavioral pathways, so an effective approach must address both.
Treating and Recovery Options for Anxiety-Related Hair Loss
Recovery focuses on reducing the trigger and restoring hair cycle stability. At Estemoon intermediary organization, we use a structured approach:
1) Assessment and Diagnosis
Medical history: stressors, illnesses, medications, weight changes, sleep patterns, menstrual cycles
Examination: dermoscopy for miniaturization or autoimmune signs
Labs where indicated: ferritin, vitamin D, TSH, zinc, B12
2) Education and Expectation Setting
In TE, shedding is delayed and often peaks before it improves
Early regrowth signs: usually 8–12 weeks; full recovery in 3–6 months, depending on the cause
If AGA is also present, maintenance therapy will be needed
3) Dual-Focus Plan (Mind + Hair)
Anxiety/stress management plus medical/cosmetic follicle support
Regular follow-up and photo documentation every 12 weeks
Sample TE recovery timeline:
| Phase | Expected | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|
| 0–4 weeks | Shedding may continue | Focus on trigger control and nutrition |
| 4–12 weeks | Shedding slows; new short hairs visible | Maintain care routine; follow stress plan |
| 3–6 months | Noticeable fullness returns | Adjust treatment if needed; stay consistent |
Medical and Cosmetic Options for Stress-Related Hair Loss
| Option | Mechanism | Suitable For | Time to Response | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Topical minoxidil (2–5%) | Extends growth phase, counters miniaturization | TE and AGA | 3–6 months | May cause initial shedding |
| Low-dose oral minoxidil | Systemic follicle stimulation | Those intolerant to topical | 3–6 months | Requires medical monitoring |
| Anti-androgen therapy* | Reduces DHT effects | AGA with stress trigger | 4–6+ months | Must be prescribed with caution |
| PRP | Growth factor stimulation | Early–moderate AGA/TE support | 3–6 months | Requires a series and maintenance |
| LLLT devices | Photobiomodulation | Men & women as adjunct | 3–6 months | Consistent use is key |
| Nutritional optimization | Corrects deficiencies | Low ferritin/vitamin D/zinc/protein | 8–12 weeks | Avoid crash diets |
| Cosmetic aids | Hair fibers, volumizing shampoos | Anyone wanting instant coverage | Immediate | Improves appearance & confidence |
* Prescription medications should be tailored to the patient and reviewed for contraindications.
How to Reduce Hair Loss by Managing Stress
Daily habits
Sleep 7–9 hours consistently
Practice breathing exercises or short meditation (5–10 minutes daily)
Engage in moderate exercise 3–4 days/week
Limit caffeine and sugar late in the day; reduce alcohol
Nutrition
Protein: 1.0–1.2 g/kg/day (up to 1.5 g/kg during recovery)
Keep ferritin, vitamin D, zinc, and B12 in optimal ranges
Eat colorful vegetables and omega-3-rich foods
Avoid rapid weight loss or extreme calorie restriction
Hair and scalp care
Avoid tight hairstyles and high heat
Use gentle, sulfate-balanced shampoo; manage dandruff if present
Light scalp massage 1–2 times/week for 2–3 minutes
Protect from sun and chlorine
Monitoring
Take baseline and 12-week follow-up photos (same lighting and angle)
Remember: shedding may peak before improvement starts
Keep a written plan for treatments and lifestyle changes
FAQ
Can anxiety cause different types of hair loss?
Yes. The most common is telogen effluvium, but anxiety can trigger trichotillomania, accelerate androgenetic alopecia, or contribute to alopecia areata flares.
Is hair loss from anxiety a permanent condition?
Usually not. TE is often reversible once the trigger is resolved. If AGA is present, maintenance therapy is required to preserve regrowth.
What is the link between cortisol and shedding?
Chronic stress raises cortisol, which can shift follicles into telogen phase and promote micro-inflammation, impacting hair growth.
How can I treat anxiety-related hair loss?
Address the stress trigger first—improve sleep, diet, exercise, and seek psychological support. Add medical hair therapies (minoxidil, LLLT, PRP) and correct any nutritional deficiencies.