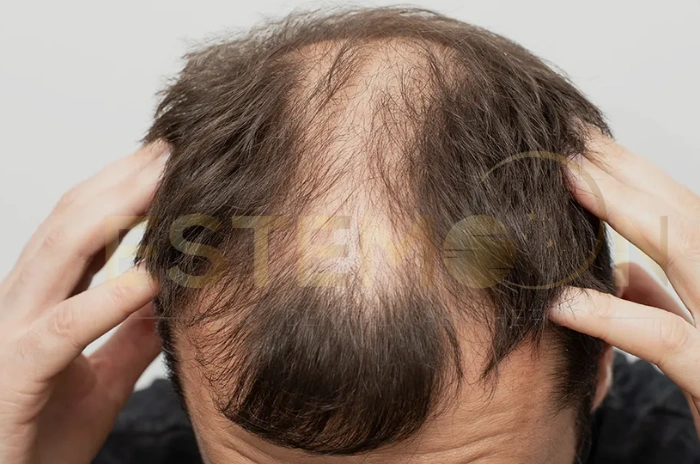
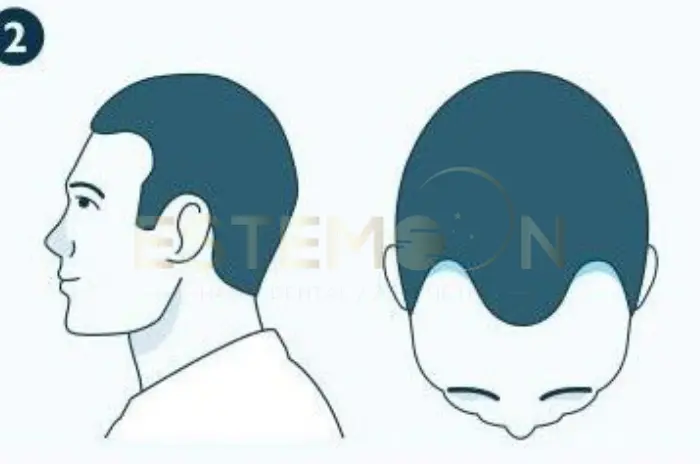
PCOS hair loss is one of the most distressing symptoms of polycystic ovary syndrome, affecting millions of women worldwide. This condition significantly affects self-esteem, mental health, and quality of life. Unlike typical hair loss patterns, PCOS hair thinning creates a unique challenge because it stems from complex hormonal imbalances that require targeted treatment approaches.
Polycystic ovary syndrome affects approximately 10% of women of reproductive age. Beyond irregular periods and fertility concerns, PCOS and hair loss symptoms create visible changes that many women find particularly difficult to cope with. This comprehensive guide will help you understand your options and take control of your PCOS hair regrowth journey.

Why PCOS leads to hair thinning in women
PCOS hair loss occurs primarily due to elevated androgen levels, particularly testosterone and dihydrotestosterone (DHT). Women with PCOS produce higher-than-normal amounts of these male hormones, which directly affect hair follicles on the scalp. This hormonal imbalance triggers androgenic alopecia PCOS, also known as PCOS female pattern baldness.
When androgen levels rise, they convert testosterone into DHT through an enzyme called 5-alpha reductase. DHT binds to receptors in hair follicles, particularly on the top and front of the scalp. This binding causes follicles to gradually shrink—a process called miniaturization. As follicles become smaller, they produce thinner, shorter, and weaker hair strands.
The pattern of PCOS hair thinning differs from typical male pattern baldness. Women with PCOS typically experience diffuse thinning across the crown and top while maintaining their frontal hairline. The hair parting becomes wider, and the scalp becomes increasingly visible.
Insulin resistance, present in approximately 70% of women with PCOS, compounds the problem. High insulin levels increase androgen production and reduce sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG), a protein that normally binds to testosterone. When SHBG levels drop, more free testosterone circulates, available to convert into DHT.
Symptoms and signs of PCOS hair thinning
Recognizing PCOS and hair loss symptoms early enables prompt intervention and better treatment outcomes. The signs develop gradually over time.
The most noticeable symptom is progressive thinning across the crown and top of the scalp. You may observe your hair part becoming wider, with more scalp visible. When you pull your hair back, you might notice the ponytail feels thinner or smaller. Under bright lighting, your scalp becomes increasingly visible.
Increased daily hair shedding represents another common sign. While normal hair loss ranges from 50-100 strands daily, women experiencing PCOS hair loss may lose significantly more. You might notice excessive hair on your pillow, in the shower drain, or on your brush.
Changes in hair texture often accompany PCOS hair loss. Individual strands become finer and more fragile. Your hair may lack body and volume, appearing limp even after styling. Hair may also break more easily during brushing.
Many women notice their hair grows more slowly or doesn’t reach previous lengths. This occurs because affected follicles spend less time in the active growth phase.
Paradoxically, while scalp hair thins, many women with PCOS experience increased facial and body hair growth (hirsutism). This occurs because elevated androgens causing scalp PCOS hair loss stimulate hair growth in areas where men typically grow hair.
Effective medical treatments for PCOS hair loss
Medical PCOS hair loss treatment addresses the hormonal imbalances underlying the condition. Several evidence-based therapies can slow or reverse PCOS hair thinning when used consistently.
Anti-androgen medications form the cornerstone of treatment. Spironolactone blocks androgen receptors and reduces testosterone production. At doses of 100-200mg daily, spironolactone can significantly slow PCOS hair thinning and promote regrowth. Results typically become visible after 6-12 months.
Oral contraceptives containing both estrogen and progestin effectively treat PCOS hair loss by suppressing ovarian androgen production and increasing SHBG levels. Specific formulations with anti-androgenic progestins like drospirenone work particularly well for PCOS hair regrowth.
Minoxidil for PCOS hair loss stimulates hair follicles and prolongs the growth phase. Available over-the-counter in 2% and 5% concentrations, minoxidil applied twice daily can improve hair density. Initial results appear after 3-4 months, with maximum benefit around 12 months.
Metformin addresses insulin resistance in PCOS. By improving insulin sensitivity, metformin indirectly reduces androgen production and may help with PCOS hair regrowth. Typical doses range from 1500-2000mg daily.
Finasteride, a DHT blocker for PCOS hair loss, inhibits the enzyme that converts testosterone to DHT. While effective for PCOS hair regrowth, this medication carries severe birth defect risks for women of childbearing potential.

Stress management to reduce PCOS related hair loss
PCOS hair loss stress management plays a crucial role in comprehensive treatment. Chronic stress significantly worsens both PCOS symptoms and hormonal imbalance hair loss. The relationship between stress and PCOS hair thinning is bidirectional—stress exacerbates hormonal imbalances, while experiencing hair loss creates additional emotional stress.
Chronic stress elevates cortisol levels, which disrupts hormone balance and increases insulin resistance. High cortisol also triggers telogen effluvium, pushing hair follicles into premature resting phases.
Mind-body practices demonstrate significant benefits. Regular meditation, even just 10-15 minutes daily, reduces cortisol levels and improves hormonal balance. Studies show that women with PCOS who practice mindfulness meditation experience reduced androgen levels.
Yoga combines physical activity with stress reduction, offering dual benefits for PCOS hair loss treatment. Regular yoga practice improves insulin sensitivity, reduces inflammation, and promotes better sleep.
Adequate sleep is essential for hormonal regulation and PCOS hair regrowth. Poor sleep worsens insulin resistance and increases cortisol production. Establishing consistent sleep schedules supports better sleep quality.
Support groups connect you with other women experiencing PCOS hair loss. Sharing experiences and emotional support reduces feelings of isolation.
Regular physical activity reduces stress, improves insulin sensitivity, and supports hormonal balance. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise weekly.
How DHT treatment helps with PCOS related hair loss
DHT blocker for PCOS hair loss treatments specifically target the hormone most directly responsible for androgenic alopecia PCOS. DHT is approximately five times more potent than testosterone at binding to androgen receptors in hair follicles.
Topical DHT blockers offer targeted treatment without systemic side effects. Natural compounds like saw palmetto, pumpkin seed oil, and green tea extract have demonstrated DHT-blocking properties. These natural DHT blockers for PCOS hair loss can be applied directly to the scalp.
Prescription DHT blockers provide more powerful effects. Finasteride and dutasteride inhibit 5-alpha reductase systemically, dramatically reducing DHT levels. While effective for PCOS hair regrowth, these medications carry significant risks for women of childbearing potential.
Combining DHT blockers with other PCOS hair loss treatment approaches enhances effectiveness. Using a topical DHT blocker alongside minoxidil for PCOS hair loss and anti-androgen medication provides multi-targeted therapy.
Home remedies to support PCOS hair regrowth
Home remedies for PCOS hair loss complement medical treatments and address nutritional, topical, and lifestyle factors that support PCOS hair regrowth. While home remedies alone rarely reverse significant PCOS hair thinning, they enhance medical interventions.
A low-glycemic diet that minimizes blood sugar spikes reduces insulin levels and subsequently lowers androgen production. Focus on lean proteins, healthy fats, abundant vegetables, and limited refined carbohydrates. Specific foods include fatty fish, nuts, seeds, eggs, leafy greens, and berries.
PCOS hair loss diet and supplements should address nutritional deficiencies. Iron supplementation benefits women with confirmed deficiency. Vitamin D supplementing with 2000-4000 IU daily improves status. Omega-3 fatty acids reduce inflammation.
Inositol improves insulin sensitivity and reduces androgen levels. Studies show that 2-4 grams of inositol daily can improve hormonal balance and support PCOS hair regrowth treatment.
Topical scalp treatments using natural oils provide nourishment. Pumpkin seed oil contains compounds that inhibit 5-alpha reductase. Rosemary oil has demonstrated hair growth stimulation. Apply these oils 2-3 times weekly.
Scalp massage improves blood circulation to hair follicles. Spend 5-10 minutes daily massaging your scalp gently.
A comprehensive PCOS hair care routine minimizes damage. Use sulfate-free, gentle shampoos. Avoid excessive heat styling and tight hairstyles.
Surgical Options for PCOS-Related Fertility
Surgical options for PCOS primarily address fertility concerns rather than PCOS hair loss directly. However, surgical interventions that improve hormonal balance may indirectly benefit PCOS hair regrowth by reducing androgen levels.
Ovarian drilling, a laparoscopic procedure, involves making small punctures in the ovaries. This procedure reduces androgen production by destroying small portions of androgen-producing tissue. While primarily performed to restore ovulation, the resulting reduction in androgen levels may support PCOS hair regrowth treatment.
The effects can persist for several months to years, potentially providing sustained improvement. However, this procedure is not specifically performed for hair loss treatment and carries surgical risks.
Treat PCOS Hair Loss Medical and Natural Options – Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main causes of PCOS hair loss?
PCOS hair loss is caused by elevated androgen hormones, particularly DHT, which shrink hair follicles through miniaturization, combined with insulin resistance and chronic inflammation.
How is PCOS hair loss treated effectively?
Effective treatment combines anti-androgen medications like spironolactone, birth control pills, minoxidil, DHT blockers, lifestyle modifications including low-glycemic diet, stress management, and targeted supplements.
Are there home remedies to help hair regrowth?
Home remedies including low-glycemic diet, omega-3 supplements, inositol, topical oils like rosemary and pumpkin seed, scalp massage, and gentle hair care practices support regrowth alongside medical treatments.
Do anti-androgen medications help with hair loss?
Yes, anti-androgen medications like spironolactone and birth control pills significantly help PCOS hair loss by blocking androgen receptors, reducing testosterone production, and increasing SHBG levels.
Follow us on social media for updates, tips, and patient success stories: