Lupus hair loss affects millions of people worldwide, creating both physical and emotional challenges for those living with this autoimmune condition. Understanding the connection between lupus and hair thinning helps patients recognize early warning signs and seek appropriate treatment before permanent damage occurs.
This comprehensive guide explores the relationship between lupus and hair health, covering everything from initial symptoms to advanced treatment options. Whether you’re experiencing your first lupus flare or managing long-term symptoms, knowing how to protect and restore your hair becomes essential for maintaining confidence and overall well-being.

What Lupus Is and How It Affects Hair
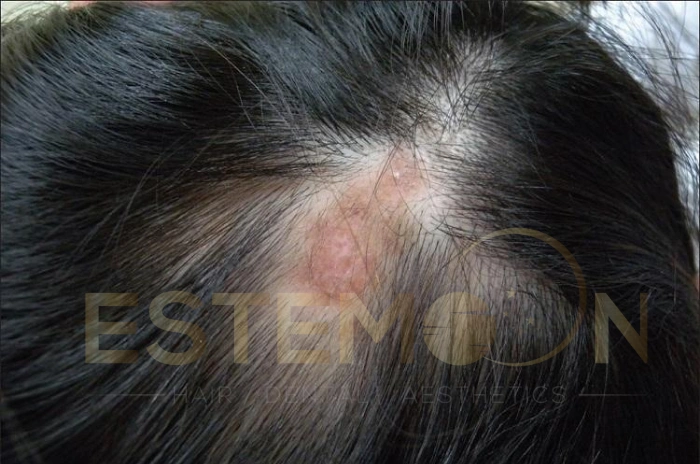
Lupus represents a complex autoimmune disorder where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissues, including hair follicles. Lupus hair loss occurs when inflammatory processes target the scalp, disrupting normal hair growth cycles and potentially causing permanent follicle damage.
The condition manifests in several forms, with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) being the most common type affecting hair. During active disease periods, inflammatory cytokines circulate throughout the body, reaching hair follicles and interfering with their normal function. This process can lead to both temporary and permanent hair loss from lupus.
How Lupus Disrupts Hair Growth
Normal hair growth occurs in three distinct phases: anagen (growth), catagen (transition), and telogen (rest). Autoimmune hair loss from lupus disrupts this cycle by:
- Shortening the anagen phase, reducing hair length and thickness
- Prolonging the telogen phase, causing increased shedding
- Creating inflammation around follicles, leading to miniaturization
- Damaging follicle stem cells, potentially causing permanent loss
Lupus symptoms hair changes often appear gradually, making early detection challenging. Many patients initially attribute hair thinning to stress, hormonal changes, or genetic factors before receiving a proper lupus diagnosis.
Spotting Early Symptoms of Hair Loss from Lupus
Recognizing early symptoms of lupus hair loss enables prompt intervention and better outcomes. Unlike typical pattern baldness, lupus-related hair changes often present with distinctive characteristics that distinguish them from other causes of hair thinning.
Primary Warning Signs
Hair thinning lupus typically begins with subtle changes that gradually become more noticeable:
- Diffuse thinning across the entire scalp rather than specific patterns
- Increased hair shedding during washing or brushing
- Shorter, more fragile hair that breaks easily
- Changes in hair texture, becoming coarser or finer
- Patchy areas of thinning, particularly around the hairline
Associated Scalp Symptoms
Scalp health lupus complications often accompany hair loss, including:
- Redness or inflammation on the scalp surface
- Scaling or flaking resembling severe dandruff
- Tenderness or sensitivity to touch
- Burning or itching sensations
- Small sores or lesions on the scalp
Lupus scalp thinning may coincide with other autoimmune symptoms such as joint pain, fatigue, skin rashes, or sun sensitivity. Patients experiencing multiple symptoms simultaneously should seek medical evaluation promptly.
Progression Patterns
Hair shedding lupus patterns help distinguish autoimmune hair loss from other conditions:
| Lupus Hair Loss | Other Hair Loss Types |
|---|---|
| Diffuse, widespread thinning | Specific pattern areas |
| Associated scalp inflammation | Usually no inflammation |
| Coincides with lupus flares | Independent of systemic symptoms |
| May include eyebrow/eyelash loss | Typically scalp-only |
| Texture changes common | Texture usually unchanged |
How to Get a Diagnosis for Lupus-Related Hair Thinning
Obtaining accurate hair loss diagnosis for lupus requires comprehensive evaluation by healthcare professionals familiar with autoimmune conditions. Early diagnosis significantly improves treatment outcomes and prevents permanent follicle damage.
Medical History and Physical Examination
Healthcare providers begin with detailed medical history, focusing on:
- Family history of autoimmune diseases
- Timeline of hair loss development
- Associated symptoms beyond hair changes
- Previous treatments attempted
- Current medications and supplements
Physical examination includes thorough scalp assessment, checking for inflammation, scarring, or other characteristic signs of lupus related alopecia.
Laboratory Testing
Treatment for lupus hair loss begins with confirming the underlying diagnosis through blood tests:
- Antinuclear antibody (ANA) testing
- Anti-double-stranded DNA antibodies
- Complement levels (C3 and C4)
- Complete blood count with differential
- Inflammatory markers (ESR and CRP)
Specialized Testing
Additional diagnostic procedures may include:
Scalp Biopsy: Microscopic examination of scalp tissue reveals inflammatory patterns characteristic of lupus hair loss. This procedure provides definitive diagnosis when blood tests remain inconclusive.
Trichoscopy: Non-invasive examination using specialized magnification identifies early changes in hair follicles and scalp condition before visible thinning occurs.
Pull Test: Simple office procedure determines whether hair shedding exceeds normal rates, helping quantify the severity of hair loss.
Types of Lupus Hair Loss Scarring and Non Scarring
Understanding different types of lupus hair treatment requires recognizing whether hair loss involves scarring or remains reversible. This distinction significantly impacts treatment options and long-term prognosis.
Non-Scarring Lupus Hair Loss
Diffuse hair loss represents the most common form of lupus-related hair thinning. This type affects the entire scalp uniformly without creating permanent follicle damage.
Characteristics include:
- Widespread thinning maintaining scalp coverage
- Reversible with proper treatment
- Hair follicles remain intact
- Often improves with lupus activity control
Hair shedding lupus in non-scarring forms typically responds well to treatment when caught early. Patients may experience significant regrowth once inflammation subsides and appropriate therapies begin.
Scarring Lupus Hair Loss (Discoid Lupus)
Discoid lupus creates permanent hair loss through follicle destruction and scarring. This more severe form requires aggressive early intervention to prevent irreversible damage.
Features of scarring lupus hair loss:
- Clearly defined patches of complete hair loss
- Visible scarring or skin texture changes
- Permanent follicle destruction
- Progressive expansion without treatment
Mixed Presentations
Some patients experience both scarring and non-scarring hair loss simultaneously, requiring comprehensive treatment approaches addressing multiple mechanisms of follicle damage.
| Non-Scarring | Scarring |
|---|---|
| Diffuse, uniform thinning | Patchy, complete loss |
| Reversible hair loss | Permanent hair loss |
| Follicles remain viable | Follicles destroyed |
| Responds to anti-inflammatory treatment | Requires aggressive early intervention |
| Good regrowth potential | Limited regrowth potential |
Using Minoxidil for Hair Regrowth in Lupus
Hair regrowth lupus treatment often includes minoxidil as a cornerstone therapy for stimulating follicle activity and promoting new hair growth. This FDA-approved medication works through multiple mechanisms particularly relevant to autoimmune hair loss.
How Minoxidil Works in Lupus Hair Loss
Minoxidil addresses lupus hair regrowth through several pathways:
- Vasodilation increases blood flow to hair follicles
- Prolongs the anagen (growth) phase of hair cycles
- Stimulates follicle miniaturization reversal
- Enhances nutrient delivery to weakened follicles
- May provide mild anti-inflammatory effects
Application Guidelines for Lupus Patients
Gentle hair care practices become essential when using minoxidil for lupus hair loss:
Morning Application:
- Apply to completely dry scalp
- Use fingertips for gentle distribution
- Avoid aggressive rubbing or massage
- Allow complete absorption before styling
Evening Application:
- Clean scalp with mild, sulfate-free shampoo
- Apply minoxidil to towel-dried hair
- Avoid heat styling after application
- Sleep on silk or satin pillowcases
Expected Timeline and Results
Lupus hair regrowth with minoxidil follows predictable patterns:
- Weeks 1-4: Initial shedding may increase temporarily
- Weeks 6-12: Shedding reduces, fine new growth appears
- Months 3-6: Visible improvement in hair density
- Months 6-12: Maximum benefit achieved
Patients should continue treatment consistently, as discontinuation results in gradual return to baseline hair loss within 3-4 months.
Treatment Options That Help With Lupus Hair Loss
Comprehensive treatment for lupus hair loss requires multifaceted approaches addressing both underlying autoimmune activity and specific hair follicle support. Successful outcomes typically involve combining systemic lupus management with targeted hair restoration therapies.
Systemic Lupus Management
Controlling overall lupus activity represents the foundation of lupus hair treatment:
Hydroxychloroquine: This antimalarial medication reduces lupus flare frequency and severity, indirectly supporting hair health by controlling systemic inflammation.
Immunosuppressive Medications: Methotrexate, azathioprine, or mycophenolate mofetil may be prescribed for severe cases with extensive hair loss.
Corticosteroids: Short-term prednisone courses can rapidly reduce scalp inflammation during acute flares, though long-term use should be avoided due to side effects.
Topical Treatments
DHT blockers hair treatments may benefit some lupus patients, particularly those with androgenetic alopecia components:
Topical Finasteride: Reduces DHT production at the follicle level without systemic absorption concerns.
Ketoconazole Shampoo: Provides anti-inflammatory effects and mild DHT blocking properties.
Topical Corticosteroids: Prescription-strength treatments for inflamed areas of the scalp.
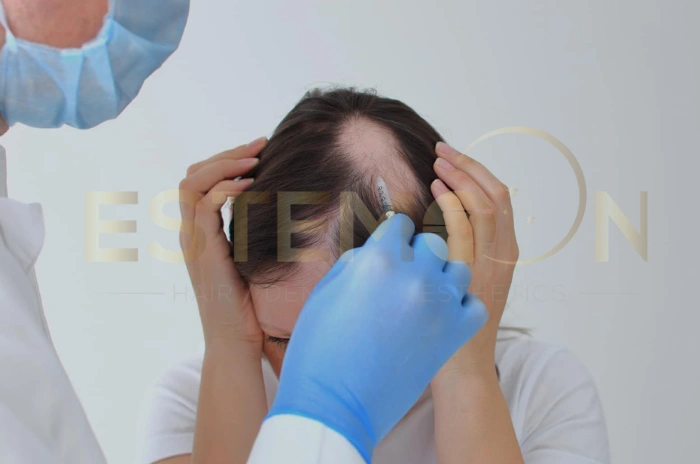
Advanced Therapies
Hair transplant lupus considerations require special evaluation:
- Disease activity must be stable for at least 12 months
- Donor area assessment for adequate healthy follicles
- Risk-benefit analysis considering ongoing immunosuppression
- Alternative procedures like scalp micropigmentation for non-candidates
Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT): FDA-approved devices may stimulate follicle activity through photobiomodulation, potentially enhancing other treatments’ effectiveness.
Nutritional Support
Lupus flare hair recovery benefits from targeted nutritional interventions:
- Iron supplementation for documented deficiency
- Biotin and B-complex vitamins for follicle health
- Omega-3 fatty acids for anti-inflammatory effects
- Vitamin D optimization for immune system balance
Lifestyle Modifications
Supporting scalp health lupus through daily practices:
- Sun protection to prevent lupus flare triggers
- Stress management techniques
- Regular sleep schedule maintenance
- Avoiding harsh chemical treatments or excessive heat styling
FAQs About Lupus hair loss signs prevention and effective treatments
What are the symptoms of lupus-related hair loss?
Lupus hair loss symptoms include diffuse thinning, increased shedding, scalp inflammation, and hair texture changes that often coincide with other autoimmune symptoms.
Can hair loss from lupus be reversed?
Hair loss from lupus can be reversed in non-scarring cases with proper treatment, though scarring forms may result in permanent loss requiring alternative restoration approaches.
How is lupus hair loss diagnosed and treated?
Hair loss diagnosis involves blood tests for autoimmune markers, scalp examination, and sometimes biopsy, with treatment combining lupus management and targeted hair therapies.
Do minoxidil and hair transplants work for lupus?
Minoxidil effectively promotes hair regrowth lupus in most patients, while hair transplant lupus procedures require stable disease and careful candidate selection for optimal results.
Follow us on social media for updates, tips, and patient success stories: