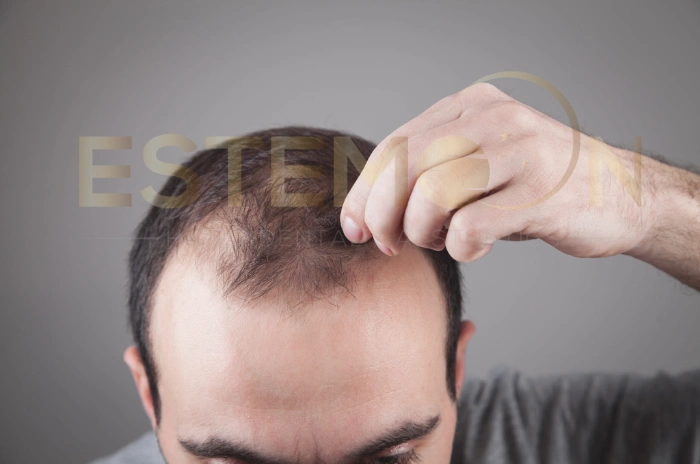
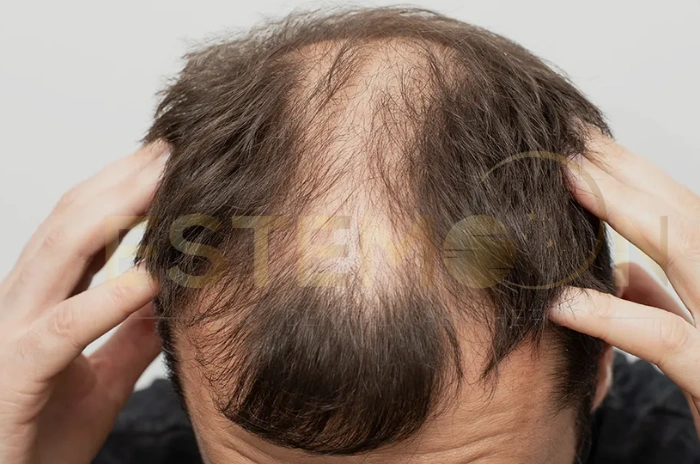
Thyroid hair loss affects millions of people worldwide, yet many remain unaware of the connection between their thyroid function and hair health. Understanding how thyroid disorders impact hair growth is crucial for proper diagnosis and effective treatment. This comprehensive guide explores the relationship between thyroid conditions and hair loss, providing essential information for those experiencing unexplained hair thinning or loss.
The thyroid gland plays a vital role in regulating metabolism, energy production, and cellular growth throughout the body. When thyroid function becomes disrupted, hair follicles are among the first structures to be affected. Both hypothyroidism hair loss and hyperthyroidism hair loss can lead to significant changes in hair texture, density, and growth patterns.
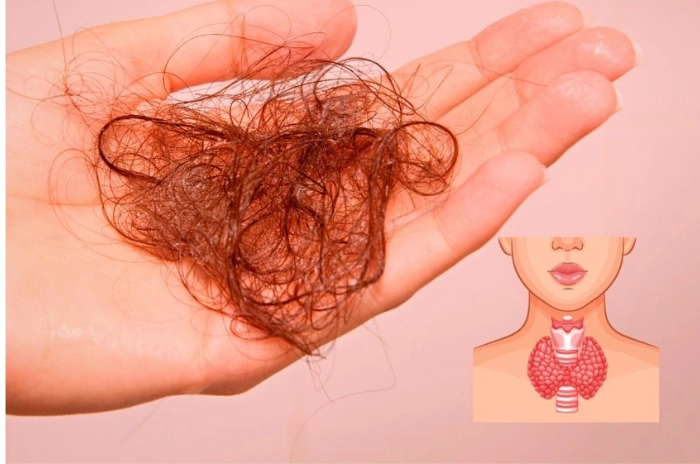

How thyroid problems cause hair loss
The thyroid gland produces hormones T3 (triiodothyronine) and T4 (thyroxine) that regulate cellular metabolism and growth processes. These hormones directly influence the hair follicle cycle, affecting how quickly hair grows and when it transitions to the resting phase.
In hypothyroidism hair loss, insufficient thyroid hormone production slows down cellular processes throughout the body. Hair follicles receive inadequate signals to produce new hair strands, leading to prolonged resting phases and reduced hair density. The existing hair often becomes dry, brittle, and prone to breakage.
Hyperthyroidism hair loss occurs when excessive thyroid hormone production accelerates the hair growth cycle unnaturally. This rapid cycling causes hair follicles to exhaust themselves prematurely, leading to telogen effluvium – a condition where large numbers of hair follicles simultaneously enter the resting phase and shed their hair.
Autoimmune thyroid disease, including Hashimoto’s thyroiditis and Graves’ disease, can trigger additional complications such as alopecia areata. This condition causes the immune system to attack hair follicles directly, creating circular patches of complete hair loss.
Diagnosing thyroid hair loss and other causes
Accurate diagnosis of thyroid and hair loss requires comprehensive evaluation by healthcare professionals. The diagnostic process typically begins with detailed medical history taking and physical examination to identify characteristic patterns and symptoms.
Blood tests form the cornerstone of thyroid hair loss diagnosis. Essential tests include TSH (thyroid-stimulating hormone), free T4, free T3, and thyroid antibodies. Additional laboratory tests may include complete blood count, ferritin levels, vitamin D, vitamin B12, and zinc levels.
| Test Type | Normal Range | Hypothyroidism | Hyperthyroidism |
|---|---|---|---|
| TSH (mIU/L) | 0.4-4.0 | >4.0 | <0.4 |
| Free T4 (ng/dL) | 0.8-1.8 | <0.8 | >1.8 |
| Free T3 (pg/mL) | 2.3-4.2 | <2.3 | >4.2 |
| Anti-TPO | <35 IU/mL | Often elevated | May be elevated |
| Ferritin (ng/mL) | 15-200 | Often low | Variable |
Dermatological examination helps distinguish thyroid-related hair loss from other conditions. Diffuse hair loss thyroid typically presents with uniform thinning across the entire scalp, whereas other conditions may show specific patterns or localized areas of hair loss.
Effective Treatments for Thyroid Hair Loss
Thyroid hair loss treatment focuses primarily on restoring optimal thyroid hormone levels through appropriate medication management. Levothyroxine remains the standard treatment for hypothyroidism, while antithyroid medications may be necessary for hyperthyroidism management.
Hormone replacement therapy requires careful monitoring and dosage adjustments. Most patients begin to notice improvements in hair texture and reduced shedding within 3-6 months of achieving stable thyroid hormone levels. Complete thyroid hair regrowth may take 6-12 months as the hair growth cycle normalizes.
Topical treatments such as minoxidil can provide additional support for hair regrowth while thyroid treatment takes effect. This FDA-approved medication helps stimulate blood flow to hair follicles and can be particularly beneficial for patients experiencing telogen effluvium related to thyroid dysfunction.
Role of supplements and biotin for hair in thyroid disorders
Biotin for thyroid hair loss has gained significant attention, though its effectiveness varies among individuals. Biotin (vitamin B7) plays a crucial role in keratin production and cellular metabolism. However, biotin supplementation requires careful consideration due to its potential to interfere with thyroid function tests.
Biotin thyroid tests can be significantly affected by high-dose biotin supplementation. Biotin interferes with many laboratory assays, potentially leading to falsely elevated or suppressed thyroid hormone results. Patients should discontinue biotin supplements at least 72 hours before thyroid function testing.
Essential nutrients for supporting hair health in thyroid patients include iron, zinc, selenium, and vitamins D and B12. Iron deficiency commonly accompanies hypothyroidism and significantly impacts hair growth. Selenium supports thyroid hormone conversion and has antioxidant properties that protect hair follicles.
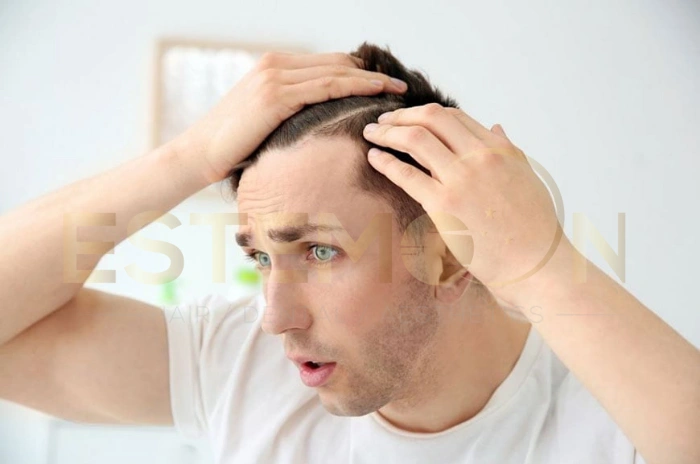

Common Symptoms of Hair Loss Linked to Thyroid Disorders
Thyroid symptoms hair loss extends beyond simple hair thinning to encompass various changes in hair texture, growth patterns, and overall scalp health. Understanding these symptoms helps patients and healthcare providers recognize thyroid-related hair issues early.
Hypothyroidism hair loss typically presents as generalized thinning across the entire scalp, with hair becoming increasingly dry, coarse, and brittle. Patients often notice increased hair breakage during brushing or washing, along with reduced hair density. The outer third of eyebrows may also thin significantly.
Hyperthyroidism hair loss manifests differently, with hair often becoming fine, soft, and prone to excessive shedding. Patients may notice handfuls of hair coming out during washing or brushing, leading to rapid and dramatic thinning.
Thyroid disorders symptoms affecting hair include changes in hair growth rate and hair color changes, with premature graying being more common in thyroid patients.
Daily Hair Care Tips for Managing Thyroid Hair Loss
Gentle hair care practices become essential when managing thyroid hair loss to minimize additional damage and support the natural regrowth process. Avoiding harsh chemicals, excessive heat styling, and aggressive brushing can help preserve existing hair while new growth develops.
Home remedies for thyroid hair loss include scalp massage to improve circulation, essential oil treatments with rosemary or peppermint oils, and regular deep conditioning treatments to maintain hair moisture. These approaches can complement medical treatment while providing psychological benefits.
Protective styling techniques help minimize breakage during daily activities. Using silk or satin pillowcases, avoiding tight hairstyles, and choosing gentle hair accessories can reduce mechanical stress on fragile hair affected by thyroid dysfunction.
Tips for Living with Thyroid Conditions
Successfully managing thyroid conditions requires a comprehensive approach that addresses both the underlying endocrine dysfunction and its various manifestations, including hair loss. Regular monitoring of thyroid hormone levels ensures optimal medication dosing and helps prevent fluctuations that can trigger hair loss episodes.
Medication adherence remains crucial for maintaining stable thyroid function and preventing thyroid medication and hair loss complications. Taking thyroid medications consistently, at the same time each day, helps optimize treatment outcomes.
Building a supportive healthcare team including endocrinologists and dermatologists provides comprehensive care for complex thyroid-related issues. Patient education empowers individuals to recognize symptoms, understand treatment goals, and actively participate in their care.
FAQs About Diagnosing Thyroid Hair Loss and Ruling Out Other Causes
What causes hair loss in thyroid disorders?
Thyroid hair loss occurs when thyroid hormone imbalances disrupt the normal hair growth cycle, causing follicles to enter resting phases prematurely.
How is thyroid-related hair loss diagnosed?
Hair loss thyroid diagnosis involves comprehensive blood tests including TSH, free T4, T3, and thyroid antibodies, combined with physical examination.
Can hair loss from thyroid problems be reversed?
Most thyroid hair regrowth is possible with proper treatment, though complete recovery may take 6-12 months after achieving optimal thyroid hormone levels.
Do biotin supplements help with thyroid hair loss?
Biotin for thyroid hair loss may provide some benefits, but high doses can interfere with thyroid function tests and should be used cautiously.
Follow us on social media for updates, tips, and patient success stories: